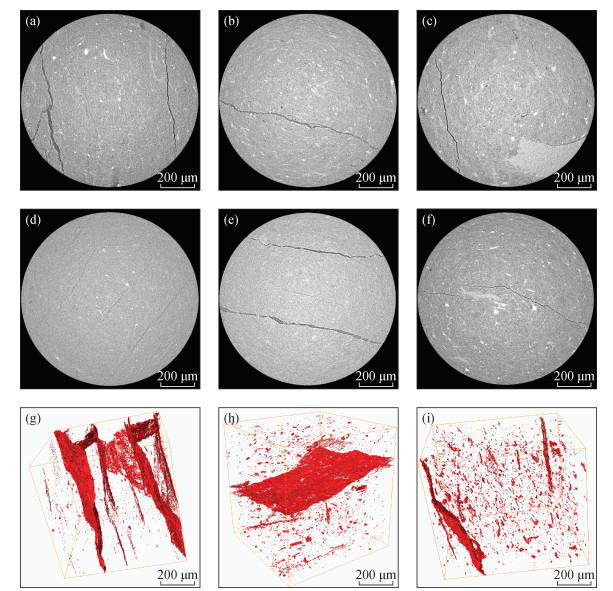
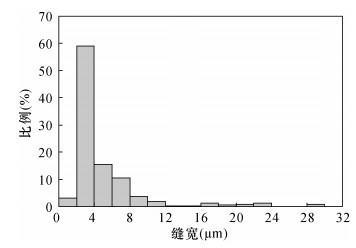
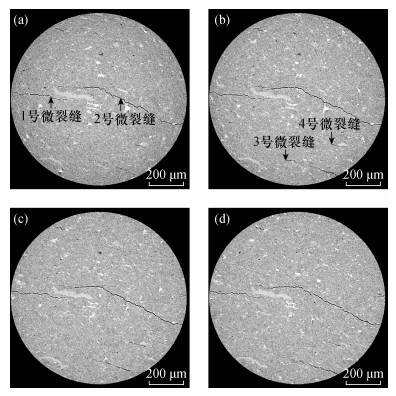
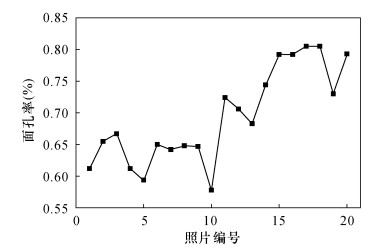
| [1] |
Hao F, Zou H Y, Lu Y C.Mechanisms of shale gas storage:Implications for shale gas exploration in China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(8):1325-1346.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
戴方尧, 郝芳, 胡海燕, 等.川东焦石坝五峰-龙马溪组页岩气赋存机理及其主控因素[J].地球科学, 2017, 42(7):1185-1194.
Google Scholar
Dai F Y, Hao F, Hu H Y, et al.Occurrence mechanism and key controlling factors of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale gas[J].Earth Science, 2017, 42(7):1185-1194.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al.Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1071-1098.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Nelson R A, Moldovanyi E P, Matcek C C, et al.Production characteristics of the fractured reservoirs of the La Paz field, Maracaibo Basin, Venezuela[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(11):1791-1809.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Zhu H, Ju Y, Huang C, et al.Pore structure variations across structural deformation of Silurian Longmaxi shale:An example from the Chuandong thrust-fold belt[J].Fuel, 2019, 241:914-932.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Gale J F W, Reed R M, Holder J.Natural fractures in the Barnett shale and their importance for hydraulic fracture treatments[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):603-622.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Rohrbaugh M B J, Dunne W M, Mauldon M.Estimating fracture trace intensity, density, and mean length using circular scan lines and windows[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(12):2089-2104.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Ortega O J, Marrett R A, Laubach S E.A scale-independent approach to fracture intensity and average spacing measurement[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(2):193-208.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Zeng L B, Su H, Tang X M, et al.Fractured tight sandstone oil and gas reservoirs:A new play type in the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(3):363-377.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Anders M H, Laubach S E, Scholz C H.Microfractures:A review[J].Journal of Structural Geology, 2014, 69:377-394.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Ougier-Simonin A, Renard F, Boehm C, et al.Microfracturing and microporosity in shales[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 162:198-226.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
李长海, 赵伦, 刘波, 等.微裂缝研究进展、意义及发展趋势[J].天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(3):402-416.
Google Scholar
Li C H, Zhao L, Liu B, et al.Research status, significance and development trend of microfractures[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(3):402-416.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Slatt R M, O'Brien N R.Pore types in the Barnett and Woodford gas shales:Contribution to understanding gas storage and migration pathways in fine-grained rocks[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(12):2017-2030.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Loucks R G, Reed R M.Natural microfractures in unconventional shale-oil and shale-gas systems:Real, hypothetical, or wrongly defined?[J].GCAGS Journal, 2016, 5:64-72.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
王玉满, 董大忠, 杨桦, 等.川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩储集空间定量表征[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2014, 44(6):1348-1356.
Google Scholar
Wang Y M, Dong D Z, Yang H, et al.Quantitative characterization of reservoir space in the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Shale, southern Sichuan, China[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2014, 44(6):1348-1356.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
王玉满, 王宏坤, 张晨晨, 等.四川盆地南部深层五峰组-龙马溪组裂缝孔隙评价[J].石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(4):531-539.
Google Scholar
Wang Y M, Wang H K, Zhang C C, et al.Fracture pore evaluation of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng to Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formations in southern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(4):531-539.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
臧士宾, 崔俊, 郑永仙, 等.柴达木盆地南翼山油田新近系油砂山组低渗微裂缝储集层特征及成因分析[J].古地理学报, 2012, 14(1):133-141.
Google Scholar
Zang S B, Cui J, Zheng Y X, et al.Analysis of characteristics of low-permeable reservoir with micro-fractureand their origins of the Neogene Youshashan Formation in Nanyishan oilfield, Qaidam Basin[J].Journal of Palaeogeography, 2012, 14(1):133-141.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
孙文峰, 李玮, 李卓, 等.页岩储层微裂缝发育程度预测方法[J].科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(19):118-123.
Google Scholar
Sun W F, Li W, Li Z, et al.Prediction method of micro-fracture development degree of shale reservoir[J].Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(19):118-123.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
董大忠, 施振生, 孙莎莎, 等.黑色页岩微裂缝发育控制因素——以长宁双河剖面五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5):763-774.
Google Scholar
Dong D Z, Shi Z S, Sun S S, et al.Factors controlling microfractures in black shale:A case study of Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Shuanghe Profile, Changning area, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(5):763-774.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
方辉煌, 桑树勋, 刘世奇, 等.基于微米焦点CT技术的煤岩数字岩石物理分析方法——以沁水盆地伯方3号煤为例[J].煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(5):167-174.
Google Scholar
Fang H H, Sang S X, Liu S Q, et al.Study of digital petrophysical analysis method based on micro-focus X-ray tomography:A case study from No.3 coal seam of Bofang mining area in southern Qinshui Basin[J].Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(5):167-174.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
王羽, 汪丽华, 王建强, 等.利用纳米CT研究石柱龙马溪组页岩有机孔三维结构特征[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(6):580-590.
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Wang L H, Wang J Q, et al.Investigation of organic matter pore structures of shale in three dimensions of shale using nano-X-ray microscopy[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(6):580-590.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
黄家国, 许开明, 郭少斌, 等.基于SEM、NMR和X-CT的页岩储层孔隙结构综合研究[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(1):198-205.
Google Scholar
Huang J G, Xu K M, Guo S B, et al.Comprehensive study on pore structures of shale reservoirs based on SEM, NMR and X-CT[J].Geoscience, 2015, 29(1):198-205.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
徐祖新, 郭少斌.基于NMR和X-CT的页岩储层孔隙结构研究[J].地球科学进展, 2014, 29(5):624-631.
Google Scholar
Xu Z X, Guo S B.Application of NMR and X-CT technology in the pore structure study of shale gas reservoirs[J].Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(5):624-631.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
张平, 王登科, 于充, 等.基于工业CT扫描的数字煤心构建过程及裂缝形态表征[J].河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 38(6):10-16.
Google Scholar
Zhang P, Wang D K, Yu C, et al.Digital coal core construction process and crack characterization based on industrial CT scanning[J].Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 2019, 38(6):10-16.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
屈乐.基于低渗透储层的三维数字岩心建模及应用[D].西安: 西北大学, 2014.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-1014364626.htm
Google Scholar
Qu L.3D Digital core modeling and application based on low permeability reservoir[D].Xi'an: Northwest University, 2014.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
屈乐, 孙卫, 杜环虹, 等.基于CT扫描的三维数字岩心孔隙结构表征方法及应用——以莫北油田116井区三工河组为例[J].现代地质, 2014, 28(1):190-196.
Google Scholar
Qu L, Sun W, Du H H, et al.Characterization technique of pore structure by 3D digital core based on CT scanning and its application:An example from Sangonghe Formation of 116 Well Field in Mobei Oilfield[J].Geoscience, 2014, 28(1):190-196.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
黄振凯, 陈建平, 王义军, 等.微米CT在烃源岩微观结构表征方面的应用[J].石油实验地质, 2016, 38(3):418-422.
Google Scholar
Huang Z K, Chen J P, Wang Y J, et al.Application of micro CT in the characterization of microstructure in source rocks[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(3):418-422.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
戚超, 王晓琦, 王威, 等.页岩储层微观裂缝三维精细表征方法[J].石油学报, 2018, 39(10):1175-1185.
Google Scholar
Qi C, Wang X Q, Wang W, et al.Three-dimensional fine characterization method of micro-fractures in shale reservoirs[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(10):1175-1185.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
陈彦君, 苏雪峰, 王钧剑, 等.基于X射线微米CT扫描技术的煤岩孔裂隙多尺度精细表征——以沁水盆地南部马必东区块为例[J].油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(5):66-72.
Google Scholar
Chen Y J, Su X F, Wang J J, et al.Multi-scale fine characterization of coal pore-fracture structure based on X-ray micro-CT scanning:A case study of Mabidong Block, southern Qinshui Basin[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(5):66-72.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等.基于微米CT页岩微裂缝表征方法研究[J].地质学报, 2019, 93(9):2372-2382.
Google Scholar
Gou Q Y, Xu S, Hao F, et al.Study on characterization of micro-fracture of shale based on micro-CT[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(9):2372-2382.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Gou Q Y, Xu S, Hao F, et al.Full-scale pores and micro-fractures characterization using FE-SEM, gas adsorption, nano-CT and micro-CT:A case study of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale in the Fuling area, Sichuan Basin, China[J].Fuel, 2019, 253:167-179.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
邹才能, 杨智, 王红岩, 等."进源找油":论四川盆地非常规陆相大型页岩油气田[J].地质学报, 2019, 93(7):1551-1562.
Google Scholar
Zou C N, Yang Z, Wang H Y, et al."Exploring petroleum inside source kitchen":Jurassic unconventional continental giant shale oil & gas field in Sichuan Basin, China[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(7):1551-1562.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
邹才能, 杨智, 孙莎莎, 等."进源找油":论四川盆地页岩油气[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2020, doi:10.1360/SSTe-2019-0246.
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zou C N, Yang Z, Sun S S, et al."Exploring petroleum inside source kitchen":Shale oil and gas in Sichuan Basin[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2020, doi:10.1360/SSTe-2019-0246.
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
肖继林, 魏祥峰, 李海军, 等.涪陵海相页岩气和元坝-兴隆场湖相页岩气富集条件差异性分析[J].天然气勘探与开发, 2018, 41(4):8-17.
Google Scholar
Xiao J L, Wei X F, Li H J, et al.Difference of accumulation conditions between Fuling marine shale gas and Yuanba-Xinglongchang lacustrine shale gas[J].Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2018, 41(4):8-17.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
魏祥峰, 黄静, 李宇平, 等.元坝地区大安寨段陆相页岩气富集高产主控因素[J].中国地质, 2014, 41(3):970-981.
Google Scholar
Wei X F, Huang J, Li Y P, et al.The main factors controlling the enrichment and high production of Da'anzhai Member continental shale gas in Yuanba area[J].Geology in China, 2014, 41(3):970-981.
Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
刘忠宝, 刘光祥, 胡宗全, 等.陆相页岩层系岩相类型、组合特征及其油气勘探意义——以四川盆地中下侏罗统为例[J].天然气工业, 2019, 39(12):10-21.
Google Scholar
Liu Z B, Liu G X, Hu Z Q, et al.Lithofacies types and assemblage features of continental shale strata and their significance for shale gas exploration:A case study of the Middle and Lower Jurassic strata in the Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(12):10-21.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
曹香妮, 姜振学, 朱德宇, 等.川东北地区自流井组陆相页岩岩相类型及储层发育特征[J].天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(12):1782-1793.
Google Scholar
Cao X N, Jiang Z X, Zhu D Y, et al.Lithofacies types and reservoir characteristics of continental shales of Ziliujing Formation in northeastern Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(12):1782-1793.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
赵梦莹.川北地区下侏罗统大安寨段页岩气藏发育特征及富集规律研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2014.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10616-1015530020.htm
Google Scholar
Zhao M Y.Research on shale gas reservoir development characteristics and enrichment regularity of Da'anzhai segment in Early Jurassic in northern Sichuan, China[D].Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
杨巍, 薛莲花, 唐俊, 等.页岩孔隙度测量实验方法分析与评价[J].沉积学报, 2015, 33(6):1258-1264.
Google Scholar
Yang W, Xue L H, Tang J, et al.Analysis and evaluation of different measuring methods for shaleporosity[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(6):1258-1264.
Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
王世谦.页岩岩心样品分析数据对比及其影响因素分析[J].天然气工业, 2020(1):160-174.
Google Scholar
Wang S Q.Correlation of shale core analysis results and its influencing factors[J].Natural Gas Industry, 2020(1):160-174.
Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
徐旭辉, 申宝剑, 李志明, 等.页岩气实验地质评价技术研究现状及展望[J].油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(1):1-8.
Google Scholar
Xu X H, Shen B J, Li Z M, et al.Status and prospect of experimental technologies of geological evaluation for shale gas[J].Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(1):1-8.
Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
王幸蒙, 姜振学, 王世骋, 等.泥页岩天然裂缝特征及其对页岩气成藏、开发的控制作用[J].科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(8):34-42.
Google Scholar
Wang X M, Jiang Z X, Wang S C, et al.Characteristics of natural fractures in shale and their control effect on shale gas accumulation and development[J].Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(8):34-42.
Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
汪虎, 何治亮, 张永贵, 等.四川盆地海相页岩储层微裂缝类型及其对储层物性影响[J].石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(1):41-49.
Google Scholar
Wang H, He Z L, Zhang Y G, et al.Microfracture types of marine shale reservoir of Sichuan Basin and its influence on reservoir property[J].Oil and Gas Geology, 2019, 40(1):41-49.
Google Scholar
|
| [44] |
王玉满, 李新景, 董大忠, 等.海相页岩裂缝孔隙发育机制及地质意义[J].天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(9):1602-1610.
Google Scholar
Wang Y M, Li X J, Dong D Z, et al.Development mechanism of fracture pores in marine shale and its geological significance[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(9):1602-1610.
Google Scholar
|
| [45] |
邹才能, 董大忠, 王玉满, 等.中国页岩气特征、挑战及前景(一)[J].石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(6):689-701.
Google Scholar
Zou C N, Dong D Z, Wang Y M, et al.Shale gas in China:Characteristics, challenges and prospects (Ⅰ)[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(6):689-701.
Google Scholar
|
| [46] |
姜伟佳.川东北大安寨段陆相页岩孔隙结构特征及储集能力评价[D].北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.
Google Scholar
Jiang W J.The pore structure characteristics and reservoir capacity evaluation of continental shale of Da'anzhai Formation in the northeast of Sichuan Basin[D].Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017.
Google Scholar
|
| [47] |
马真乾, 王英滨, 于炳松, 等.渝东南地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩孔径分布测试方法研究[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3):244-255.
Google Scholar
Ma Z Q, Wang Y B, Yu B S, et al.Study on analytical method for pore size distribution of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation shale in southeastern Chongqing[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3):244-255.
Google Scholar
|
| [48] |
刘振庄, 白名岗, 杨玉茹, 等.龙马溪组页岩不同显微形态有机质成因及其勘探潜力探讨[J].岩矿测试, 2020, 39(2):199-207.
Google Scholar
Liu Z Z, Bai M G, Yang Y R, et al.Discussion on the genesis and exploration potential of eifferent microscopic forms of organic matters in the Longmaxi Formation shale[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(2):199-207.
Google Scholar
|
| [49] |
彭嫦姿, 彭俊, 陈燕辉, 等.四川盆地元坝地区大安寨段页岩气"甜点"地震预测[J].天然气工业, 2014, 34(6):42-47.
Google Scholar
Peng C Z, Peng J, Chen Y H, et al.Seismic prediction of sweet spots in the Da'anzhai shale play, Yuanba area, the Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(6):42-47.
Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: