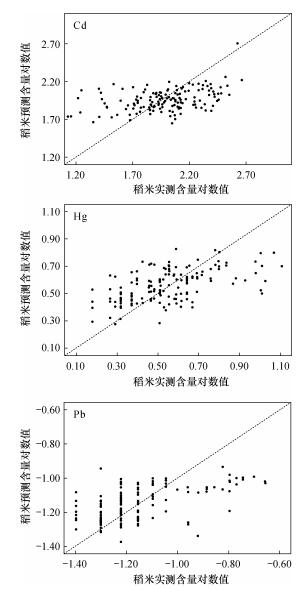
| [1] |
王瑶瑶, 郝毅, 张洪, 等.珠三角地区大米中的镉砷污染现状及治理措施[J].中国农学通报, 2019, 35(12):63-72.
Google Scholar
Wang Y Y, Hao Y, Zhang H, et al.Cadmium and arsenic pollution in rice in the pearl river delta and the counter measures[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(12):63-72.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
胡培松.土壤有毒重金属镉毒害及镉低积累型水稻筛选与改良[J].中国稻米, 2004(2):10-12.
Google Scholar
Hu P S.Cadmium detoxification in soil and breeding of new rice with less cadmium accumulation[J].China Rice, 2004(2):10-12.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
刘君, 张猛, 张士荣, 等.山东省水稻产地土壤重金属污染风险评价[J].青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 36(2):112-118.
Google Scholar
Liu J, Zhang M, Zhang S R, et al.Pollution risk evaluation of heavy metals in paddy soils in Shandong Province[J].Journal of Laiyang Agricultural College (Natural Sciences Edition), 2019, 36(2):112-118.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
杭小帅, 周健民, 王火焰, 等.常熟市高风险区水稻籽粒重金属污染特征及评价[J].中国环境科学, 2009, 29(2):130-135.
Google Scholar
Hang X S, Zhou J M, Wang H Y, et al.Heavy metal pollution characteristics and assessment of rice grain from a typical high risk area of Changshu City, Jiangsu Province[J].China Environmental Science, 2009, 29(2):130-135.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Sun G X, Wiele T Ⅴ D, Alava P, et al.Arsenic in cooked rice:Effect of chemical, enzymatic and microbial processes on bioaccessibility and speciation in the human gastrointestinal tract[J].Environmental Pollution, 2012, 162:241-246. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.11.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Chen T, Liu X, Zhu M, et al.Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban-rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2008, 151(1):67-78. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.03.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
甘国娟, 朱晓龙, 刘妍, 等.田间条件下Pb在土壤-水稻中的迁移特征[J].环境化学, 2015, 34(3):514-519.
Google Scholar
Gan G J, Zhu X L, Liu Y, et al.Transfer characteristics of Pb in soil-rice system under field conditions[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(3):514-519.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Usman A, Kuzyakov Y, Stahr K.Effect of clay minerals on immobilization of heavy metals and microbial activity in a sewage sludge-contaminated soil[J].Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2005, 5(4):245-252. doi: 10.1065/jss2005.05.141
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Ok Y S, Lim J E, Moon D H.Stabilization of Pb and Cd contaminated soil sand soil quality improvements using waste oyster shells[J].Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2011, 33(1):83-91. doi: 10.1007/s10653-010-9329-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Moreno A M, Quintana J R, Pérez L, et al.Factors influencing lead sorption-desorption at variable added metal concentrations in Rhodoxeralfs[J].Chemosphere, 2006, 64:758-763. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.10.058
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Vega F A, Covelo E F, Andrade M L.Competitive sorption and desorption of heavy metals in mine soils:Influence of mine soil characteristics[J].Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2006, 298(2):582-592.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Halim M, Conte P, Piccolo A.Potential availability of heavy metals to phytoextraction from contaminated soils induced exogenous humic substances[J].Chemosphere, 2003, 52(1):265-275. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00185-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Romero F M, Villalobos M, Aguirre R, et al. Solid-phase control on lead bioaccessibility in smelter-impacted soils[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2008, 55:566-575. doi: 10.1007/s00244-008-9152-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Ajmone-Marsan F, Biasioli M, Kralj T, et al.Metals in particle-size fractions of the soils of five European cities[J].Environmental Pollution, 2008, 152(1):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.05.020
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Luo X S, Yu S, Li X D.Distribution, availability, and sources of trace metals in different particle size fractions of urban soils in Hong Kong:Implications for assessing the risk to human health[J].Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159:1317-1326. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.01.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Madrid F, Diaz-Barrientos E, Madrid L.Availability and bio-accessibility of metals in the clay fraction of urban soils of Sevilla[J].Environmental Pollution, 2008, 156(3):605-610. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2008.06.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Qian J, Shan X Q, Wang Z J, et al.Distribution and plant availability of heavy metals in different particle-size fractions of soil[J].The Science of the Total Environment, 1996, 187:131-141. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(96)05134-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
李杰, 朱立新, 康志强.南宁市郊周边农田土壤-农作物系统重金属元素迁移特征及其影响因素[J].中国岩溶, 2018, 37(1):43-52.
Google Scholar
Li J, Zhu L X, Kang Z Q.Characteristics of transfer and their influencing factors of heavy metals in soil-crop system of peri-urban agricultural soils of Nanning, South China[J].Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(1):43-52.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
王腾云, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 等.福建沿海地区土壤-稻谷重金属含量关系与影响因素研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(3):295-301.
Google Scholar
Wang T Y, Zhou G H, Sun B B, et al.The relationship between heavy metal contents of soils and rice in coastal areas, Fujian Province, including influencing factors[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(3):295-301.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
蒋彬, 张慧萍.水稻精米中铅镉砷含量基因型差异的研究[J].云南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 22(3):37-40.
Google Scholar
Jiang B, Zhang H P.Genotypic differences in concentrations of plumbum, cadmium and arsenicum in polished rice grains[J].Journal of Yunnan Normal University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2002, 22(3):37-40.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
夏蔓蔓, 何腾兵.土壤-水稻镉生物有效性预测模型研究进展[J].天津农业科学, 2019, 25(2):12-17.
Google Scholar
Xia M M, He T B.Research progresses on prediction models of cadmium bioavailability in soil-rice system[J].Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 25(2):12-17.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Adams M L, Zhao F J, Mcgrath S P, et al. Predicting cadmium concentrations in wheat and barley grain using soil properties[J].Journal of Environmental Quality, 2004, 33(2):532-541. doi: 10.2134/jeq2004.5320
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
McBride M.Cadmium uptake by crops estimated from soil total Cd and pH[J].Soil Science, 2002, 167(1):62-76.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
刘情, 陈红燕, 唐豆豆, 等.苏南典型区土壤-水稻系统中重金属迁移特征及定量模型研究[J].环境科技, 2016, 29(4):20-25.
Google Scholar
Liu Q, Chen H Y, Tang D D, et al.Migration characteristics and quantitative model of heavy metals in the typical polluted areas of Southern Jiangsu Province[J].Environment Science and Technology, 2016, 29(4):20-25.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
赵科理, 傅伟军, 戴巍.浙江省典型水稻产区土壤-水稻系统重金属迁移特征及定量模型[J].中国生态农业学报, 2016, 24(2):226-234.
Google Scholar
Zhao K L, Fu W J, Dai W.Characteristics and quantitative model of heavy metal transfer in soil-rice systems in typical rice production areas of Zhejiang Province[J].Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(2):226-234.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
李志博, 骆永明, 宋静, 等.基于稻米摄入风险的稻田土壤镉临界值研究:个案研究[J].土壤学报, 2008(1):76-81.
Google Scholar
Li Z B, Luo Y M, Song J, et al.Critical values for Cd in paddy field based on Cd risk of rice consumption:A case study[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008(1):76-81.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
陈永胜.多元线性回归建模以及MATLAB和SPSS求解[J].绥化学院学报, 2007, 27(6):166-168.
Google Scholar
Chen Y S.Multiple linear regression modeling and MATLAB and SPSS solving[J].Journal of Suihua University, 2007, 27(6):166-168.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Kempen B, Bres D J, Heuvelink G B.Updating the 1:50000 Dutch soil map using legacy soil data:A multinomial logistic regression approach[J].Geoderma, 2009, 151(3-4):311-326. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.04.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
王梦梦, 何梦媛, 苏德纯, 等.稻田土壤性质与稻米镉含量的定量关系[J].环境科学, 2018, 39(4):1918-1925.
Google Scholar
Wang M M, He M Y, Su D C, et al.Quantitative relationship between paddy soil properties and cadmium content in rice grains[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4):1918-1925.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
何燕, 周国华, 王学求.从微量元素与人体健康关系得到的启示[J].物探与化探, 2008, 32(1):70-74.
Google Scholar
He Y, Zhou G H, Wang X Q.The enlightenment from the relationship between trace elements and human health[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(1):70-74.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Zhang H K, Shao D D, Zheng L N, et al.Determination of trace mercury in water by on-line solid phase extraction and ultraviolet vapor generation-ICP-MS[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 40(2):37-41. doi: 10.46770/AS.2019.02.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Oral E Ⅴ.Comparison of modified tessier and revised BCR sequential extraction procedures for the fractionation of heavy metals in malachite ore samples using ICP-OES[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 40(4):122-126. doi: 10.46770/AS.2019.04.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Liu M T, Mao X F, Liu J X.Direct determination of ultratrace arsenic in blood samples using an in-situ dielectric barrier discharge trap coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 40(3):83-90. doi: 10.46770/AS.2019.03.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Chen H Y, Teng Y G, Lu S J, et al.Contamination fea-tures and health risk of soil heavy metals in China[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 512-513:143-153.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
陈俊坚, 张会化, 刘鉴明, 等.广东省区域地质背景下土壤表层重金属元素空间分布特征及其影响因子分析[J].生态环境学报, 2011, 20(4):646-651.
Google Scholar
Chen J J, Zhang H H, Liu J M, et al.Spatial distributions and controlled factors of heavy metals in surface soils in Guangdong based on the regional geology[J].Ecology and Environmnet, 2011, 20(4):646-651.
Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
Chen J S, Wei F S, Zheng C J, et al.Background concen-trations of elements in soils of China[J].Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 1991, 57-58(1):699-712.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
李婷婷, 刘子宁, 朱鑫, 等.珠三角地区土壤重金属元素异常来源浅析及其环境质量评价[J].国土资源导刊, 2016, 13(2):30-35.
Google Scholar
Li T T, Liu Z N, Zhu X, et al.Origin of heavy metal element anomalies in soils of the Pearl River Delta and its environmental quality assessment[J].Land & Resources Herald, 2016, 13(2):30-35.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
韩志轩, 王学求, 迟清华, 等.珠江三角洲冲积平原土壤重金属元素含量和来源解析[J].中国环境科学, 2018, 38(9):3455-3463.
Google Scholar
Han Z X, Wang X Q, Chi Q H, et al.Occurrence and source identification of heavy metals in the alluvial soils of Pearl River Delta region, South China[J].China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(9):3455-3463.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
王开峰, 彭娜, 王凯荣, 等.长期施用有机肥对稻田土壤重金属含量及其有效性的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2008, 22(1):105-108.
Google Scholar
Wang K F, Peng N, Wang K R, et al.Effects of long-term manure fertilization on heavy metal content and its availability in paddy soils[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 22(1):105-108.
Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
周国华.土壤重金属生物有效性研究进展[J].物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1097-1106.
Google Scholar
Zhou G H.Recent progress in the study of heavy metal bioavailability in soil[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6):1097-1106.
Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
陈穗玲, 李锦文, 邓红梅.福建沿海地区农田土壤理化性质与重金属含量的关系[J].湖北农业科学, 2014, 53(13):3025-3029.
Google Scholar
Chen S L, Li J W, Deng H M.The relationship between physical and chemical properties of soil and heavy metal content in Fujian coastal farmland[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 53(13):3025-3029.
Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
刘全东, 蒋代华, 高利娟, 等.畜禽粪便有机肥源重金属在土壤-蔬菜系统中累积、迁移规律的研究进展[J].土壤通报, 2014, 45(1):252-256.
Google Scholar
Liu Q D, Jiang D H, Gao L J, et al.Research progress on heavy metal accumulation and migration of livestock dung organic fertilizer in soil-vegetable system[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2014, 45(1):252-256.
Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
王龙龙, 郭笃发, 李桥.土壤-植物系统重金属污染研究[J].绿色科技, 2013(6):236-238.
Google Scholar
Wang L L, Guo D F, Li Q.Study on heavy metal pollution in soil-plant system[J].Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2013(6):236-238.
Google Scholar
|
| [44] |
聂呈荣, 林初夏, 杜瑞英, 等.佛山市菜园地土壤及蔬菜重金属含量特征分析[J].佛山科学技术学院学报(自然科学版), 2010(3):1-5.
Google Scholar
Nie C R, Lin C X, Du R Y, et al.Heavy metal characteristics of vegetables and their soils in Foshan city[J].Journal of Foshan University(Natural Science Edition), 2010(3):1-5.
Google Scholar
|
| [45] |
吴迪, 杨秀珍, 李存雄, 等.贵州典型铅锌矿区水稻土壤和水稻中重金属含量及健康风险评价[J].农业环境科学学报, 2013, 32(10):1992-1998.
Google Scholar
Wu D, Yang X Z, Li C X, et al.Concentrations and health risk assessments of heavy metals in soil and rice in zinc-lead mining area in Guizhou Province, China[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2013, 32(10):1992-1998.
Google Scholar
|
| [46] |
付洪波, 李取生, 骆承程.珠三角滩涂围垦农田土壤和农作物重金属污染[J].农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(6):1142-1146.
Google Scholar
Fu H B, Li Q S, Luo C C.Heavy metals pollution in the reclaimed tidal flat soils and crops in the Pearl River Delta[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2009, 28(6):1142-1146.
Google Scholar
|
| [47] |
何江华, 柳勇, 王少毅, 等.广州市菜园土主要蔬菜重金属背景含量的研究[J].生态环境, 2003, 12(3):269-272.
Google Scholar
He J H, Liu Y, Wang S Y, et al.Studies on the background levels of heavy metals in major vegetables in Guangzhou vegetable garden soils[J].Ecology and Environment, 2003, 12(3):269-272.
Google Scholar
|
| [48] |
李波, 青长乐, 周正宾, 等.肥料中氮磷和有机质对土壤重金属的影响及治污中的应用[J].重庆环境科学, 2000, 22(6):37-40.
Google Scholar
Li B, Qing C L, Zhou Z B, et al.Influence of N, P and organic matter of fertilizers on heavy metals in soil and its application[J].Chongqing Environmental Science, 2000, 22(6):37-40.
Google Scholar
|
| [49] |
何电源.关于稻田施用石灰的研究[J].土壤学报, 1992, 29(1):87-93.
Google Scholar
He D Y.A review about studies on liming of paddy soil[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1992, 29(1):87-93.
Google Scholar
|
| [50] |
孙彬彬, 周国华, 刘占元, 等.黄河下游山东段沿岸土壤中重金属元素异常的成因[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(2):265-270.
Google Scholar
Sun B B, Zhou G H, Liu Z Y, et al.Origin of heavy metal anomalies in soils along the Shandong reach of the lower Yellow River, China[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(2):265-270.
Google Scholar
|
| [51] |
刘兰英, 黄薇, 吕新, 等.田间环境下土壤-水稻系统重金属的迁移特征[J].福建农业学报, 2018, 33(1):66-72.
Google Scholar
Liu L Y, Huang W, Lü X, et al.Migration of heavy metals from soil to rice plant[J].Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 33(1):66-72.
Google Scholar
|
| [52] |
Nan Z R, Li J J, Zhang J M, et al.Cadmium and zinc interactions and their transfer in soil-crop system under actual field conditions[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2002, 285(1-3):187-195. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00919-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [53] |
Yanai J, Zhao F J, McGrath S, et al. Effect of soil characteristics on Cd uptake by the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens[J].Environmental Pollution, 2006, 139(1):67-75.
Google Scholar
|
| [54] |
Lavado R S, Rodrlguez M, Alvarez R, et al.Transfer of potentially toxic elements from biosolid-treated soil stomaize and wheat crops[J].Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2007, 118(1/4):312-318.
Google Scholar
|
| [55] |
Karami M, Afyuni M, Khoshgoftarmanesh A H, et al.Grain zinc, iron, and copper concentrations of wheat grown in central Iran and their relationships with soil and climate variables[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(22):10876-10882. doi: 10.1021/jf902074f
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [56] |
Romkens P F A M, Guo H Y, Chu C L, et al.Prediction of cadmium uptake by brown rice and derivation of soil-plant transfer models to improve soil protection guidelines[J].Environmental Pollution, 2009, 157(8-9):2435-2444. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.03.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [57] |
Dudka S, Piotrowska M, Terelak H.Transfer of cadmium, lead, and zinc from industrially contaminated soil to crop plants:A field study[J].Environmental Pollution, 1996, 94(2):181-188. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(96)00069-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [58] |
曾翔, 张玉烛, 王凯荣, 等.不同品种水稻糙米含镉量差异[J].生态与农村环境学报, 2006, 22(1):67-69.
Google Scholar
Zeng X, Zhang Y Z, Wang K R, et al.Genotype difference of brown rices in Cd content[J].Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2006, 22(1):67-69.
Google Scholar
|
| [59] |
李正文, 张艳玲, 潘根兴, 等.不同水稻品种籽粒Cd、Cu和Se的含量差异及其人类膳食摄取风险[J].环境科学, 2003, 24(3):112-115.
Google Scholar
Li Z W, Zhang Y L, Pan G X, et al.Grain contents of Cd, Cu and Se by 57 rice cultivars and the risk significance for Human dietary uptake[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Science, 2003, 24(3):112-115.
Google Scholar
|
| [60] |
郭健, 姚云, 赵小旭, 等.粮食中重金属铅离子、镉离子的污染现状及对人体的危害[J].粮食科技与经济, 2018, 43(3):33-35, 85.
Google Scholar
Guo J, Yao Y, Zhao X X et al.Pollution status of lead and cadmium ions in grain and its harm to human[J].Grain Technology and Economy, 2018, 43(3):33-35, 85.
Google Scholar
|
| [61] |
刘建明, 亓昭英, 刘善科, 等.中微量元素与植物营养和人体健康的关系[J].化肥工业, 2016, 43(3):85-90.
Google Scholar
Liu J M, Qi Z Y, Liu S K, et al. Relationship between medium and trace elements and plant nutrition and human health[J].Journal of the Chemical Fertilizer Industry, 2016, 43(3):85-90.
Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: