| [1] |
芶盛, 岳宗玉, 邸凯昌, 等.火星表面含水矿物探测进展[J].遥感学报, 2017, 21(4):531-548.
Google Scholar
Gou S, Yue Z Y, Di K C, et al.Advances in aqueous minerals detection on Martian surface[J].Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 21(4):531-548.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
杨燕, 夏群科, 冯敏.名义上无水矿物中水的原位变温红外光谱研究[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(2):566-578.
Google Scholar
Yang Y, Xia Q K, Feng M.In situ FTIR investigations on noninally anlydrous minerals at varying temperatures[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(2):566-578.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
盛英明, 龚冰, 李万财, 等.名义上无水矿物中微量结构水的分析方法研究进展[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2016, 46(4):443-453.
Google Scholar
Sheng Y M, Gong B, Li W C, et al.Methodological progresses on trace amounts of structural water in noninally anlydrous minerals[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2016, 46(4):443-453.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
王志海, 叶美芳, 董会, 等.流体包裹体盐度低温拉曼光谱测定方法研究[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(6):813-821.
Google Scholar
Wang Z H, Ye M F, Dong H, et al.Determining salinity of fluid inclusions by cryogenic Raman spectroscopy[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(6):813-821.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
何佳乐, 潘忠习, 冉敬.激光拉曼光谱法在单个流体包裹体中的应用进展[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(4):383-391.
Google Scholar
He J L, Pan Z X, Ran J.Research progress on the application of laser Raman spectroscopy in single fluid inclusions[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(4):383-391.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
张蓓莉, Schwarz D.世界主要彩色宝石产地研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 2012.
Google Scholar
Zhang B L, Schwarz D.Geographic Origin Determination of Colored Gemstones[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2012.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
陈银汉, 陈卫, 陈燕.我国红宝石, 蓝宝石及其包裹体[J].矿物学报, 1991(4):298-304. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.04.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Chen Y H, Chen W, Chen Y.China's ruby and sapphire and their inclusions[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1991(4):298-304. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1991.04.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
杨坤彬, 彭金辉, 张世敏, 等.红、蓝宝石热处理现状及前景[J].贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 22(2):215-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5269.2005.02.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yang K B, Peng J H, Zhang S M, et al.Advance and prospect on heat treatment of ruby and sapphire[J].Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 2005, 22(2):215-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5269.2005.02.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Wang W Y, Scarratt K, Emmtt J L, et al.The effects of heat treatment on zircon inclusions in Madagascar[J].Gems & Gemology, 2006, 42(2):134-150.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Pardieu V, Saeseaw S, Detroyat S, et al.GIA lab reports on low-temperature heat treatment of Mozambique ruby[EB/OL].https://www.gia.edu/gia-news-research-low-temperature-heat-treatment-mozambique-ruby.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Tasnare S, Bbuwadol W, Tbanong L.Phase transforma-tion of epigenetic iron staining:Indication of low-temperature heat treatment in Mazambique ruby[J].The Journal of Gemmology, 2016, 35(2):156-161. doi: 10.15506/JoG.2016.35.2.156
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
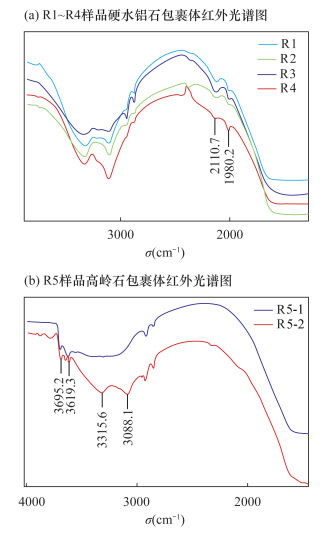
丘志力.宝石中的包裹体——宝石鉴定的关键[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 1998:45-46.
Google Scholar
Qiu Z L.Inclusions of Gemstones-The Key Identification[M].Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press, 1988:45-46.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Schwarz D.宝石学中确定宝石原产地的分析方法——以不同成因的红宝石为例[C]//2009中国珠宝首饰学术交流会论文集.北京: 国家珠宝玉石质量监督检验中心, 2009.http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_7710165.aspx
Google Scholar
Schwarz D.Analytical Methods Used for Origin Determination in Gemology (Case Study: Rubies Originating from Different Host Rocks)[C]//Proceedings of 2009 China Gems & Jewelry Academic Conference.Beijing: National Gemstone Testing Center, 2009.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
惠鹤九, 徐永江, 潘明恩.名义上无水矿物的水含量及其地质应用[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2016, 46(5):639-656.
Google Scholar
Hui H J, Xu Y J, Pan M E.On water in noninally anlydrous minerals from mantle peridotites and magmatic rocks[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2016, 46(5):639-656.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
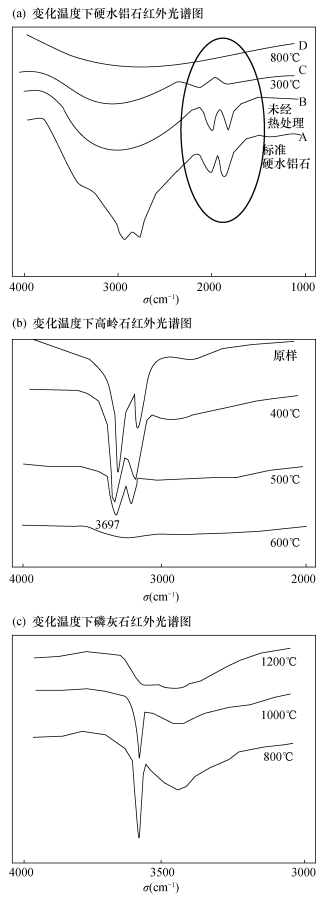
彭文世, 刘高魁.矿物热转变的红外光谱研究[J].景德镇陶瓷, 1988(4):38-42.
Google Scholar
Peng W S, Liu G K.The study of thermal transformation in minerals[J].Jingde Ceramics, 1988(4):38-42.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
吕夏.河南省中西部石炭系铝土矿中硬水铝石的矿物学特征研究[J].地质论评, 1988, 34(4):293-301. Lü X. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1988.04.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
韩秀伶, 陈开惠.高岭石-多水高岭石演化系列的红外吸收光谱研究[J].地质科学, 1982(1):71-79.
Google Scholar
Han X L, Chen K H.Study of infrared absorption spectra on the kaolinite-halloysite evolutionary series[J].Chinese Journal of Geology, 1982(1):71-79.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
彭文世, 刘高魁, 柯丽琴.某些磷灰石矿物的红外吸收光谱[J].矿物学报, 1986(1):28-37.
Google Scholar
Peng W S, Liu G K, Ke L Q.Infrared absorption spectra of some apatite minerals[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1986(1):28-37.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
刘才群.用红外光谱法研究铝矾土矿物[J].中国陶瓷, 1994(1):12-16.
Google Scholar
Liu C Q.A study on bauxitil clay mineral with infrared spectrometry[J].China Ceramics, 1994(1):12-16.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
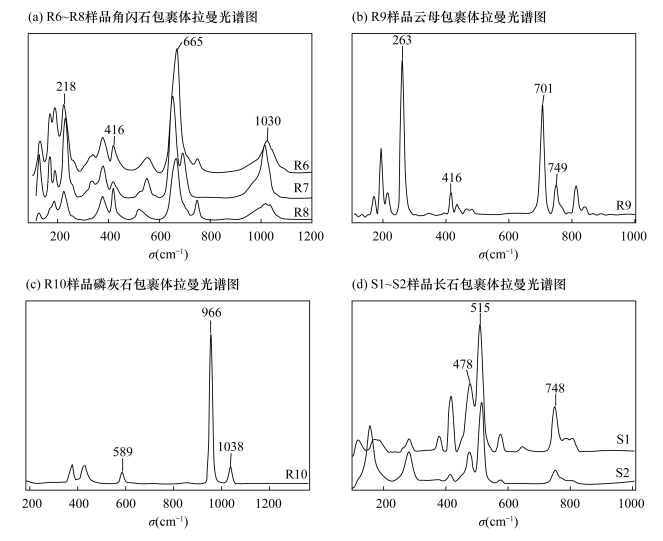
刘劲鸿.福建马坑铁矿中角闪石的谱学特征及成因意义[J].矿物岩石, 1988(1):20-30.
Google Scholar
Liu J H.Spectroscopical characteristics and genetical significance of amphiboles in the Makeng iron ore deposit[J].Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 1988(1):20-30.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
顾芷娟, 张流.围压3千巴、温度700℃时角闪石羟基的变化[J].地震地质, 1982, 4(3):83-84.
Google Scholar
Gu Z J, Zhang L.The change of hydroxyl in hornblende at confining pressure 3kb and temperature 700℃[J].Seismology and Geology, 1982, 4(3):83-84.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Aines R D, Rossman G R.The high temperature behavior of trace hydrous components in silicate minerals[J].American Mineralogist, 1985, 70:1169-1179.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
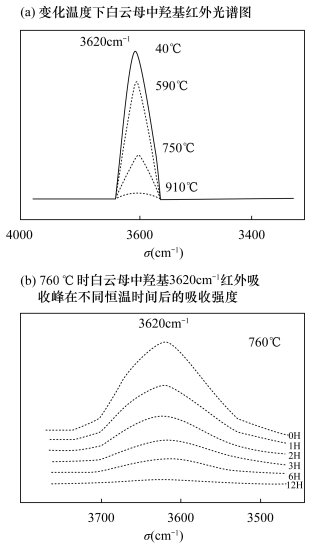
Tokiwai K, Nakashima S.Dehydration kinetics of mus-covite by in situ infrared microspectroscopy[J].Physics & Chemistry of Minerals, 2010, 37(2):91-101.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
曹淑慧, 张立飞, 孙樯, 等.高压下多硅白云母的拉曼光谱学研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2006, 25(1):71-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2006.01.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
Cao S H, Zhang L F, Sun Q, et al.A Raman spectroscopic study of phengite under high pressure[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2006, 25(1):71-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2006.01.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
张蓓莉.系统宝石学(第二版)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2006.
Google Scholar
Zhang B L.Systematic Gemmology[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2006.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
刘羽.磷灰石振动光谱的研究现状[J].武汉工程大学学报, 2002, 24(1):21-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2002.01.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
Liu Y.Review on the vibrational spectroscopy of apatites[J].Journal of Wuhan Institute of Chemical Technology, 2002, 24(1):21-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2002.01.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
屈树新, Dewijn R.羟基磷灰石生物陶瓷体外溶解实验的拉曼光谱分析[J].光散射学报, 1995(2):170-171.
Google Scholar
Qu S X, Dewijn R.Laser Raman analysis of HA in vitro[J].Chinese Journal of Light Scattering, 1995(2):170-171.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
白利平, 杜建国, 刘巍, 等.高温高压下含水矿物脱水对斜长岩纵波速度的影响[J].地质科技情报, 2003(2):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.02.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
Bai L P, Du J G, Liu W, et al.Effects of dehydration on the p-wave velocity of anorthosite at high pressure and high temperature[J].Geological Science and Technology Infomation, 2003(2):17-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.02.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Abraham J S D.Heat treating corundum:The Bangkok operation[J].Gems & Gemology, 1982, 18(2):79-82.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
刘学良.云南红宝石的宝石学特征及改善工艺研究[D].上海: 华东理工大学, 2011.http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y2011350
Google Scholar
Liu X L.Research on Gemological Characteristics and Enhancement Process of Rubies from Yunnan Province[D].Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2011.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
郑越.缅甸红宝石热处理工艺及其机理研究[D].上海: 同济大学, 2014.http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/D582742
Google Scholar
Zheng Y.Mechanism Study on Rubies of Myanmar and Its Heat Treatment Techniques[D].Shanghai: Tongji University, 2014.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
张恩, 彭明生.优化处理的红、蓝宝石中包裹体的变化和应用[J].矿产与地质, 2002, 16(1):40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2002.01.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang E, Peng M S.The changes of inclusions in ruby and sapphire after treatment and enhancement and its applications[J].Mineral Resources and Geology, 2002, 16(1):40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2002.01.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: