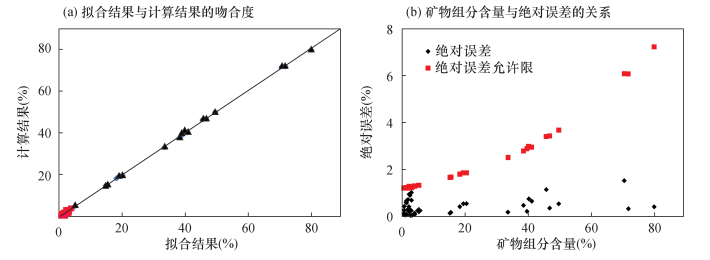
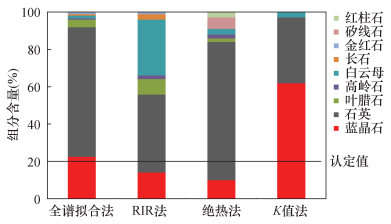
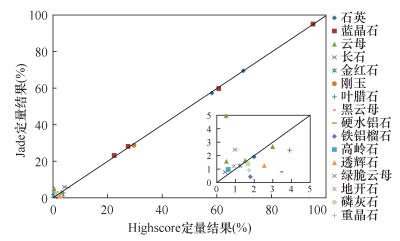
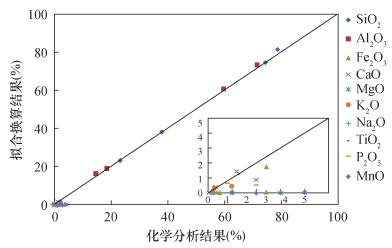
| [1] |
王梅英.蓝晶石的化学物相分析[J].非金属矿, 2006, 29(1):15-16.
Google Scholar
Wang M Y.Chemical phase analysis of cyanite[J].Non-Metallic Mines, 2006, 29(1):15-16.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
王梅英, 李鹏程, 李艳华, 等.蓝晶石矿中氟钠镁铝硅铁钛钾钙元素的X射线荧光光谱分析[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(6):909-914. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.06.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang M Y, Li P C, Li Y H, et al.Analysis of F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, Fe, Ti, K and Ca in cyanite ores by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(6):909-914. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.06.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
杜晓冉, 智红梅, 张金矿, 等.X射线衍射法定量分析蓝晶石样品[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2013, 49(4):402-404.
Google Scholar
Du X R, Zhi H M, Zhang J K, et al.Quantitative analysis of kyanite sample with X-ray diffractometry[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2013, 49(4):402-404.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
邱贤荣, 齐砚勇, 唐志强.全谱拟合定量分析石灰石[J].分析科学学报, 2013, 29(1):146-148.
Google Scholar
Qiu X R, Qi Y Y, Tang Z Q.Rietveld quantitative analysis of limestone[J].Journal of Analytical Science, 2013, 29(1):146-148.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
冉敬, 杜谷, 王凤玉.X射线衍射全谱拟合法快速分析长石矿物含量[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):489-494.
Google Scholar
Ran J, Du G, Wang F Y.Rapid analysis of feldspar by X-ray diffractometry Rietveld refinement method[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):489-494.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
迟广成, 肖刚, 汪寅夫, 等.铁矿石矿物组分的X射线粉晶衍射半定量分析[J].冶金分析, 2015, 35(1):38-44.
Google Scholar
Chi G C, Xiao G, Wang Y F, et al.Semi-quantitative analysis of the mineral components of iron ores by X-ray powder diffraction[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(1):38-44.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
洪汉烈, 陈建军, 杨淑珍, 等.水泥熟料定定量分析的全谱拟合法[J].分析测试学报, 2001, 20(2):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2001.02.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Hong H L, Chen J J, Yang S Z, et al.Quantitative phase analysis of cement clinker by Rietveld full pattern fitting method[J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2001, 20(2):5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4957.2001.02.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Gualtieri M L, Romagnoli M, Miselli P, et al.Full quantitative phase analysis of hydrated lime using the Rietveld method[J].Cement & Concrete Research, 2012, 42(9):1273-1279.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Santini T C.Application of the Rietveld refinement method for quantification of mineral concentrations in bauxite residues (alumina refining tailings)[J].International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2015, 139:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2015.04.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Woodruff L, Cannon W F, Smith D B, et al.The distribu-tion of selected elements and minerals in soil of the conterminous United States[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 154:49-60. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Gentili S, Comodi P, Bonadiman C, et al.Mass balance vs Rietveld refinement to determine the modal composition of ultramafic rocks:The case study of mantle peridotites from Northern Victoria Land (Antarctica)[J].Tectonophysics, 2015, 650:144-155. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.01.024
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
肖松.河南隐山蓝晶石矿物成因的研究[J].中国矿业, 2005, 14(2):47-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2005.02.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
Xiao S.On mineral genesis of Yinsan kyanite in Henan[J].China Mineral Magazine, 2005, 14(2):47-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2005.02.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
李锁成, 张松林, 火军昌, 等.萨尔哈布塔勒蓝晶石矿床地质及矿物学特征[J].矿产保护与利用, 2015(1):12-15.
Google Scholar
Li S C, Zhang S L, Huo J C, et al.The process mineralogy and geological characters of Saerhabutale Kyanite deposit in Gansu Province[J].Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2015(1):12-15.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
万红波, 廖立兵.膨润土中蒙脱石物相的定量分析[J].硅酸盐学报, 2009, 37(12):2055-2060. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2009.12.017
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wan H B, Liao L B.Quantitative phase analysis of montmorillonite in bentonite[J].Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2009, 37(12):2055-2060. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2009.12.017
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
房俊卓, 张霞, 徐崇福.实验条件对X射线衍射物相定量分析结果的影响[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(1):60-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.01.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
Fang J Z, Zhang X, Xu C F.Effect of experimental conditions on X-ray diffractometric quantitative phase analysis[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(1):60-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.01.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
马礼敦.X射线粉末衍射的新起点——Rietveld全谱拟合[J].物理学进展, 1996, 16(2):251-271. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0542.1996.02.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
Ma L D.The new starting point of X-ray powder diffraction-Rietveld whole pattern fitting[J].Progress in Physics, 1996, 16(2):251-271. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0542.1996.02.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
林伟伟, 宋友桂.沉积物中X射线衍射物相定量分析中的两种方法对比研究[J].地球环境学报, 2017, 8(1):83-86.
Google Scholar
Lin W W, Song Y G.A comparative study on X-ray diffraction mineral quantitative analysis of two methods in sediments[J].Journal of Earth Enviroment, 2017, 8(1):83-86.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
伍月, 刘欣, 张波, 等.X射线粉晶衍射基体清洗法在矿物定量分析中的应用[J].地质与资源, 2017, 26(3):323-328.
Google Scholar
Wu Y, Liu X, Zhang B, et al.The application and research of X-ray powder diffraction matrix flushing method in quantitative analysis[J].Geology and Resources, 2017, 26(3):323-328.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
施倪承, 白文吉, 马喆生, 等.西藏罗布莎铬铁矿床中的金刚石包体X射线衍射研究[J].地质学报, 2002, 76(4):496-500. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2002.04.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
Shi N C, Bai W J, Ma Z S, et al.A study of X-ray diffraction of diamond inclusions from Luobusha, Tibet[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2002, 76(4):496-500. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2002.04.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
王德强, 王辅亚, 王冠鑫, 等.钾含量对白云母X射线衍射特征的影响[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2004, 28(1):69-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2004.01.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang D Q, Wang F Y, Wang G X, et al.XRD character of muscovites with different potassium contents[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2004, 28(1):69-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2004.01.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
杜谷, 王坤阳, 冉敬, 等.红外光谱/扫描电镜等现代大型仪器岩石矿物鉴定技术及其应用[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(5):625-633. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.05.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
Du G, Wang K Y, Ran J, et al.Application of IR/SEM and other modern instruments for mineral identification[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(5):625-633. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.05.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: