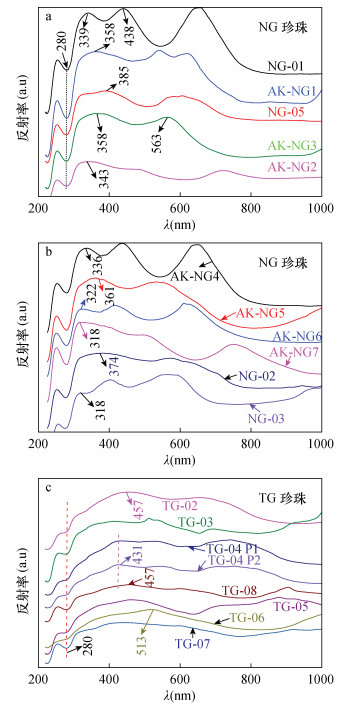
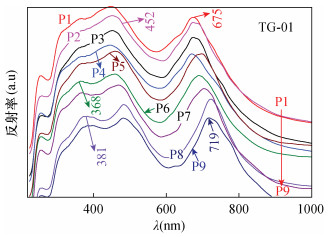
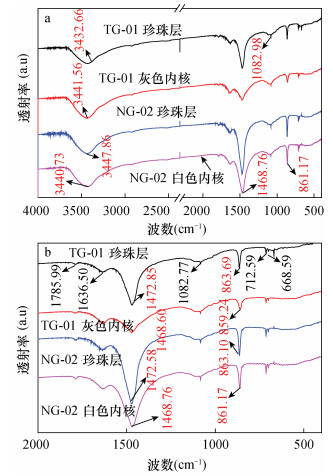
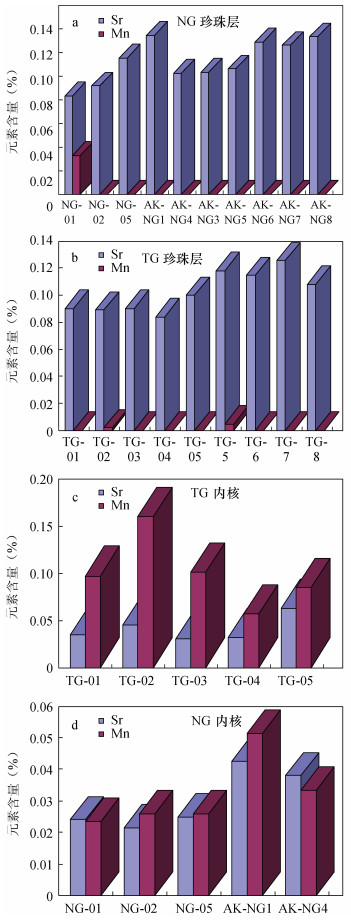
| [1] |
张蓓莉.系统宝石学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1997.
Google Scholar
Zhang B L.Systematic Gemmology[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1997.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Kripa V, Mohamed K S, Appukuttan K K, et al.Pro-duction of Akoya pearls from the southwest coast of India[J].Aquaculture, 2007, 262(2):347-354.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
宋彦军, 张义丞, 武云龙, 等.银灰色马氏贝海水珍珠的光谱学特征与颜色成因[J].矿物学报, 2017, 37(6):712-716.
Google Scholar
Song Y J, Zhang Y C, Wu Y L, et al.Spectra characteristics and coloration mechanism of silver-gray color seawater cultured pearls produced by Pinctada Martensii[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2017, 37(6):712-716.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Tadashi T.The change of pearl colors by the irradiation with γ-ray or neutron ray[J].Journal of Radiation Research, 1963, 4(2-4):120-125. doi: 10.1269/jrr.4.120
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
李立平, 杨明星.带染色核海水养殖珍珠的鉴别[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2005, 7(2):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2005.02.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Li L P, Yang M X.Identificatin of sweater cultured pearls with dyed nucleus[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2005, 7(2):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2005.02.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
亓利剑, 黄艺兰, 曾春光.各类金色海水珍珠的呈色属性及UV-Vis的反射光谱[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2008, 10(4):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2008.04.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
Qi L J, Huang Y L, Zeng C G.Colouration attributes and UV-Vis reflection spectra of various golden seawater cultured pearls[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2008, 10(4):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2008.04.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
刘雯雯, 李立平.珍珠的金黄色染色工艺及染色珍珠的鉴定[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2007, 9(4):33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2007.04.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
Liu W W, Li L P.Technology and identification of golden dyed pearls[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2007, 9(4):33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2007.04.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
董珺慧, 王以群, 史凌云, 等.黑色珍珠的无机染色[J].华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 39(2):172-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3080.2013.02.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
Dong J H, Wang Y Q, Shi L Y, et al.Inorganic dyeing of black pearl[J].Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 39(2):172-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3080.2013.02.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
郭倩, 徐志.天然金珍珠和染色金珍珠的致色因素和鉴定分析方法研究进展[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5):512-519.
Google Scholar
Guo Q, Xu Z.Coloring factors of naturall and dyed golden pearls and research progress on their identification methods[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(5):512-519.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Matsuda Y.Effects of γ-irradiation on color and fluo-rescence of pearls[J].Civil Engineering Infrastructures Journal, 1988, 27(2):235-239.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Kim H Y, Hanifehpour Y, Narayan A, et al.Structural studies and optical properties of pearl nucleus irradiated by γ-ray[J].Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids, 2013, 168(9):696-704. doi: 10.1080/10420150.2012.761997
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Kim H Y, Min B K, Jeong W G.Effects of γ-ray irra-diation on the color of pearl nucleus[J].Journal of Architecture Planning & Environmental Engineering, 2011, 27(3):247-252.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Kim Y C, Choi H, Lee B, et al.Identification of irradia-ted south sea cultured pearls using electron spin resonance spectroscopy[J].Gems & Gemology, 2012, 48(4):292-299.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Elen S.Update on the identification of treated golden south sea cultured pearls[J].Gems & Gemology, 2002, 38(2):156-159.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Elen S.Spectral reflectance and fluorescence characteri-stics of natural-color and heat-treated golden south sea cultured pearls[J].Gems & Gemology, 2001, 37(2):114-123.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
陈育, 郭守国, 史凌云.光谱学在金黄色海水珍珠鉴定中的应用[J].光学学报, 2009, 29(6):1706-1709.
Google Scholar
Chen Y, Guo S G, Shi L Y.Application of spectroscopy in identification of golden saltwater pearl[J].Acta Optica Sinica, 2009, 29(6):1706-1709.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
严俊, 陶金波, 邓小琼, 等.金色海水养殖珍珠异常的UV-Vis反射与FTIR光谱特征[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2014, 34(5):1206-1210. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)05-1206-05
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yan J, Tao J B, Deng X Q, et al.The unique reflection spectra and IR characteristics of gold-color seawater cultured pearl[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34(5):1206-1210. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)05-1206-05
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
李立平, 陈钟惠.养殖珍珠的辐照处理[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2002, 4(3):16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2002.03.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
Li L P, Chen Z H.Irradiation treatment of cultured pearls[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2002, 4(3):16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2002.03.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Yan J, Zhang J, Tao J B, et al.Origin of the common UV absorption feature in cultured pearls and shells[J].Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52(14):8362-8369. doi: 10.1007/s10853-017-1111-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
张刚生, 李浩璇.生物成因文石与无机成因文石的FTIR光谱区别[J].矿物岩石, 2006, 26(1):1-4.
Google Scholar
Zhang G S, Li H X.The FTIR spectra difference between biogenic and abiogenic aragonites[J].Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 26(1):1-4.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Pokroy B, Quintana J P, Caspi E N, et al.Anissotropic lattice distortions in biogenic aragonite[J].Natural Materials, 2004, 3(12):900-902. doi: 10.1038/nmat1263
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Pokroy B, Fieramosca J S, von Dreele R B, et al.Atomic structure of biogenic aragonite[J].Chemistry Materials, 2007, 19(13):3244-3251. doi: 10.1021/cm070187u
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
严俊, 刘培钧, 张旭, 等.海水养殖金色珍珠独特的吸收光谱及其微结构[J].上海大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 20(6):707-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2861.2014.06.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yan J, Liu P J, Zhang X, et al.Unique absorption spectrum and microstructure characteristics of golden seawater cultured pearl[J].Journal of Shanghai University (Natural Science), 2014, 20(6):707-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2861.2014.06.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
严俊, 胡仙超, 王巨安, 等.不同颜色的淡水养殖珍珠呈色机理研究[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(2):263-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.02.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yan J, Hu X C, Wang J A, et al.Investigation on the coloring mechanism of freshwater cultured pearls with different color[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(2):263-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.02.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
张刚生, 丁世磊, 贾太轩, 等.珍珠及贝壳珍珠层文石的异常红外光谱特征[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2005, 7(3):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2005.03.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang G S, Ding S L, Jia T X, et al.Unusual characteristics of FTIR spectra aragonites from nacreous layers of pearls and bivalve shells[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2005, 7(3):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2005.03.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Habermann D, Banerjee A, Meijer J, et al.Investigation of manganese in salt- and freshwater pearls[J].Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 2001, 181(1):739-743.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
木士春, 马红艳.养殖珍珠微量元素特征及其对珍珠生长环境的指示意义[J].矿物学报, 2001, 21(3):551-553. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.03.069
CrossRef Google Scholar
Mu S C, Ma H Y.Trace element characteristics of cultured pearls and their indicating meaning for growth environment of pearls[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2001, 21(3):551-553. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2001.03.069
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
兰延, 张珠福, 张天阳.荧光能谱技术鉴别淡水珍珠和海水珍珠的应用[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2010, 12(4):31-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2010.04.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Lan Y, Zhang Z F, Zhang T Y.Identification of saltwater cultured pearls and freshwater cultutred pearls by using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopic technique[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2010, 12(4):31-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2010.04.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Zhang E, Huang F Q, Wang Z T, et al.Characteristics of trace elements in freshwater and seawater cultured pearls[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34(9):2544-2547.
Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: