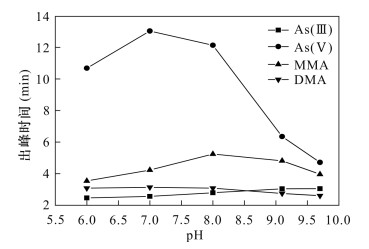
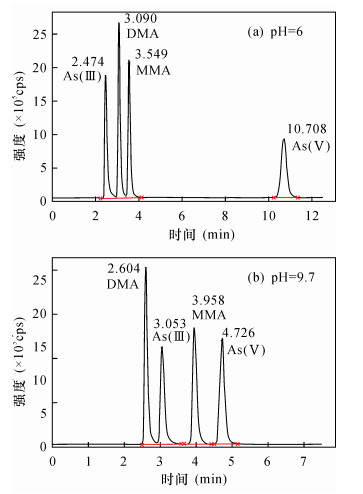
| [1] |
Hirata S, Toshimitsu H.Determination of arsenic species and arsenosugars in marine samples by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2007, 21:447-454.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Mcsheehy S, Szpunar J, Morabito R, et al.The speciation of arsenic in biological tissues and the certification of reference materials for quality control[J].Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2003, 22(4):191.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Francesconi K A, Kuehnelt D.Determination of arsenic species:A critical review of methods and applications, 2000-2003[J].Analyst, 2004, 129:373-395.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
张静, 刘晓端, 江林.土壤中不同形态砷的分析方法[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 37(3):179-183.
Google Scholar
Zhang J, Liu X D, Jiang L.Speciation analysis of arsenic in soil[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 37(3):179-183.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
袁建, 王亚平, 许春雪, 等.地下水中砷形态标准物质研制[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(2):331-337.
Google Scholar
Yuan J, Wang Y P, Xu C X, et al.The development of arsenic speciation reference material in ground water[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(2):331-337.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
严秀平, 倪哲明.联用技术应用于元素形态分析的新进展[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2003, 23(5):945-954.
Google Scholar
Yan X P, Ni Z M.New advances in application of combined technology to element species analysis[J].Spectroscopy and Spectroscopic Analysis, 2003, 23(5):945-954.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Cullen W R, Reimer K J.Arsenic speciation in the environment[J].Chemical Reviews, 1989, 89(1):713-764.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
何红蓼, 倪哲明, 李冰, 等.环境样品中痕量元素的化学形态分析Ⅱ:砷汞镉锡铅硒铬的形态分析[J].岩矿测试, 2005, 24(2):118-128.
Google Scholar
He H L, Ni Z M, Li B, et al.Trace elemental speciation in environmental samples Ⅱ:Speciation of As, Hg, Cd, Sn, Pb, Se and Cr[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2005, 24(2):118-128.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Chen S, Zhu S, Lu D.Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction coupled with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for speciation of antimony in environmental water samples by electrothermal vaporization ICP-MS[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(2):55-61.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Soleo L, Lovreglio P, Lacvicoli S, et al.Significance of urinary arsenic speciation in assessment of seafood ingestion as the main source of organic and inorganic arsenic in a population resident near a coastal area[J].Chemosphere, 2008, 73:291-299.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Karthikeyan S, Hirata S.Ion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry determination of arsenic species in marine samples[J].Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2004, 18:323-330.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
杨正标, 陆喜红, 任兰, 等.HPLC-ICP-MS法测定地表水体中砷的形态[J].化学分析计量, 2015, 24(1):37-39.
Google Scholar
Yang Z B, Lu X H, Ren L, et al.Determination of arsenic species in water by high performance liquid chromatography and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Chemical Analysis and Mererage, 2015, 24(1):37-39.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Komorowicz I, Sajnog A, Baralkiewicz D.Total arsenic and arsenic species determination in freshwater fish by ICP-DRC-MS and HPLC/ICP-DRC-MS techniques[J].Molecules, 2019, 24(3):607-625.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Son S H, Lee W B, Kim D H, et al.An alternative analytical method for determining arsenic species in rice by using ion chromatography and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Food Chemistry, 2019, 270(1):353-358.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
刘崴, 胡俊栋, 杨红霞, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定禽类生物样品中7种砷形态[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2017, 53(3):299-304.
Google Scholar
Liu W, Hu J D, Yang H X, et al.Determination of seven arsenic species in poultry biological sample by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2017, 53(3):299-304.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
白云飞.土壤底泥中砷形态提取与水样中砷形态保存实验研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2007.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-2007066966.htm
Google Scholar
Bai Y F.An Experimental Research on Preservation of Arsenic Species in Water Samples and Extraction of the Speciation from Soils and Sediments[D].Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2007.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
陈绍占, 刘丽萍, 杜宏举, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法分析经牛黄解毒片暴露后大鼠血清中砷形态[J].质谱学报, 2017, 38(2):177-186.
Google Scholar
Chen S Z, Liu L P, Du H J, et al.Arsenic species in rat serum after oral adiministration of Niuhuang Jiedu tablet by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2017, 38(2):177-186.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
王林裴, 郑亚哲, 彭新然.HPLC-ICP-MS法测定水产动物及其制品中5种砷形态的含量[J].食品与机械, 2017, 33(11):61-66.
Google Scholar
Wang L P, Zheng Y Z, Peng X R.Determination of five arsenic species in aquatic animals and their products by high performance liquid chromatoraphy and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Food and Machinery, 2017, 33(11):61-66.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Slejkovec Z, Falnoga I, Goessler W, et al.Analytical artefacts in the speciation of arsenic in clinical samples[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2008, 607:83-91.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
侯艳霞, 刘丽萍, 潘浩, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱分析大米中砷形态化合物[J].分析试验室, 2013, 32(10):103-107.
Google Scholar
Hou Y X, Liu L P, Pan H, et al.Determination of arsenic species in rice by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2013, 32(10):103-107.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
方军, 舒永红, 滕久委, 等.HPLC-ICP-MS测定中药中砷的形态[J].分析试验室, 2007, 26(9):34-37.
Google Scholar
Fang J, Shu Y H, Teng J W, et al.Determination of arsenic speciation in traditional Chinese medicine using HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2007, 26(9):34-37.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
倪张林, 汤富彬, 屈明华, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱联用技术测定花茶中砷形态[J].分析科学学报, 2013, 29(4):506-510.
Google Scholar
Ni Z L, Tang F B, Qu M H, et al.Determination of arsenic species in scented tea by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Science, 2013, 29(4):506-510.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
黄红霞.离子色谱分离-电感耦合等离子体质谱联用法测定肉类食品中无机砷[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2010, 46(10):1122-1124.
Google Scholar
Huang H X.ICP-MS determination of inorganic arsenic in meat food with IC separation[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2010, 46(10):1122-1124.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
韩梅, 赵国兴, 李淑珍, 等.毛细管电泳-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地下水中不同形态的砷[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(11):1780-1781.
Google Scholar
Han M, Zhao G X, Li S Z, et al.Speciation analysis of arsenic in groundwater by capillary electrophoresis-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(11):1780-1781.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
杨林, 于珊.碰撞反应电感耦合等离子体质谱法直接测定卤水中的溴碘[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(3):502-505.
Google Scholar
Yang L, Yu S.Direct measurement of Br and I in brines by collision response-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(3):502-505.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
姜贞贞, 刘高令, 王祝, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定高海拔地区地热水中的微量元素[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5):475-480.
Google Scholar
Jiang Z Z, Liu G L, Wang Z, et al.Determination of trace elements in thermomineral waters of a high altitude area by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(5):475-480.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
贾娜, 韩梅, 李科, 等.离子色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定地下水中4种形态砷的含量[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2016, 52(3):292-295.
Google Scholar
Jia N, Han M, Li K, et al.IC-ICP-MS determination of 4 arsenic species in groundwater[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2016, 52(3):292-295.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
吴思霖, 王欣美, 于建, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱联用测定肌肉及鸡肝中10种砷形态化合物[J].分析测试学报, 2018, 37(4):482-486.
Google Scholar
Wu S L, Wang X M, Yu J, et al.Determination of ten arsenic species compounds in chicken and chicken liver by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2018, 37(4):482-486.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Wangkarn S, Spiros A.High-speed separation of arsenic compounds using narrow-bore high-performance liquid chromatography on-line with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2000, 15(6):627-633.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Raimund W.HPLC-ICP-MS快速、准确测定鱼肉组织中的砷甜菜碱(AsB)[J].中国环境监测, 2004, 20(6):67-72.
Google Scholar
Raimund W.Rapid and accurate determination of arsenic betaine (AsB) in fish tissue by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Environmental Monitoring in China, 2004, 20(6):67-72.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
邹昊辰.硅藻土负载铁氧化物对砷吸附的研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2013.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1013193599.htm
Google Scholar
Zou H C.Study on Adsorption of Arsenic by Diatomite Coated Iron Oxide[D].Changchun: Jilin University, 2013.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
张秀尧, 蔡欣欣, 张晓艺, 等.离子色谱-三重四极杆质谱联用法测定奶粉中氟乙酸钠[J].质谱学报, 2019, 40(1):90-96.
Google Scholar
Zhang X Y, Cai X X, Zhang X Y, et al.Determination of sodium monofluoroacetate in dairy powders by ion chromatography-triple quadrpole mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2019, 40(1):90-96.
Google Scholar
|





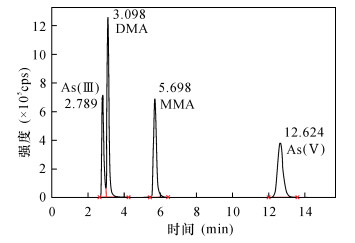

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: