| [1] |
樊连杰, 裴建国, 赵良杰, 等.利用ICP-MS研究桂林寨底地下河系统中碳酸盐岩稀土元素特征及其形成环境[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(3):251-258.
Google Scholar
Fan L J, Pei J G, Zhao L J, et.al.Rare earth element composition of carbonate rocks afforded by ICP-MS and formation environment of the Zhaidi underground river in Guilin[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(3):251-258.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
刘菁钧, 赖子娟, 刘颖.黄河甘宁蒙段表层沉积物中稀土元素形态和分馏作用研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(3):798-803. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)03-0798-06
CrossRef Google Scholar
Liu J J, Lai Z J, Liu Y.Study on speciation and fractionation of rare earth elements in surface sediments in Gansu, Ningxia and Inner Mongolia Sections of Yellow River[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Anaylsis, 2013, 33(3):798-803. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)03-0798-06
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
刘丽君, 赵芝, 付小方, 等.四川稀土矿尾砂的稀土元素和微量元素地球化学特征及开发利用意义[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(5):817-824. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.05.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
Liu L J, Zhao Z, Fu X F, et al.Geochemistry of rare earth and trace element in rare earth tailings from Sichuan Province and the significance of the exploitation and utilization[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(5):817-824. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.05.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Zhang Y, Gao X L, Arthur C, et al.Rare earth elements in intertidal sediments of Bohai Bay, China:Concentration, fractionation and the influence of sediment texture[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014, 105:72-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
程建忠, 车丽萍.中国稀土资源开采现状及发展趋势[J].稀土, 2010, 31(2):65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.02.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
Cheng J Z, Che L P.Current mining situation and potential development of rare earth in China[J].Chinese Rare Earths, 2010, 31(2):65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2010.02.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Mittermüller M, Saatz J, Daus B.A sequential extraction procedure to evaluate the mobilization behavior of rare earth elements in soils and tailings materials[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 147:155-162. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.12.101
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Gabarrón M, Faz A, Martínez-Martínez S, et al.Assess-ment of metals behaviour in industrial soil using sequential extraction, multivariable analysis and a geostatistical approach[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 172:174-183. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.10.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Nemati K, Bakar N K A, Abas M R, et al.Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192:402-410.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Rao C R M, Sahuquillo A, Lopez-Sanchez J F.Compari-son of single and sequential extraction procedures for the study of rare earth elements remobilisation in different types of soils[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2010, 662(2):128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
王亚平, 黄毅, 王苏明, 等.土壤和沉积物中元素的化学形态及其顺序提取法[J].地质通报, 2005, 24(8):728-734. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.08.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang Y P, Huang Y, Wang S M, et al.Chemical speciation of elements in sediments and soils and their sequential extraction process[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2005, 24(8):728-734. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.08.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Gleyzes C, Tellier S, Astruc M.Fractionation studies of trace elements in contaminated soils and sediments: A review of sequential extraction procedures[J].2002, 21(6): 451-467.
http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e8857058b6da1459db6129d0176f956d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
王立军, 王玉琦, 章申, 等.中国不同类型土壤中稀土元素的形态分布特征[J].中国稀土学报, 1997, 15(1):65-71.
Google Scholar
Wang L J, Wang Y Q, Zhang S, et al.Speciation of rare earth elements in different types of soils in China[J].Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 1997, 15(1):65-71.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Šmuc N R, Dolenec T, Serafimovski T, et al.Geochemi-cal characteristics of rare earth elements (REEs) in the paddy soil and rice (Oryza sativa L.) system of Koc ǎni Field, Republic of Macedonia[J].Geoderma, 2012, 183-184:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.03.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
郭鹏然, 贾晓宇, 段太成, 等.土壤中稀土元素的形态分析[J].分析化学, 2008, 36(11):1483-1487. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2008.11.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Guo P R, Jia X Y, Duan T C, et al.Speciation analysis of rare earth elements in soil[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 36(11):1483-1487. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2008.11.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
翟海, 杨永岗, 胡霭堂.对我国二十种土壤中稀土元素形态分组的研究[J].稀土, 2001, 22(3):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2001.03.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhai H, Yang Y G, Hu A T.Study of rare earths fractionation in 20 types of soils of China[J].Chinese Rare Earths, 2001, 22(3):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2001.03.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
郭伟, 付瑞英, 赵仁鑫, 等.内蒙古包头白云鄂博矿区及尾矿区周围土壤稀土污染现状和分布特征[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(5):1895-1900.
Google Scholar
Guo W, Fu R Y, Zhao R X, et al.Distribution characteristics and current situation of soil rare earth contamination in the Bayan Obo Mining Area and Baotou tailing reservoir in Inner Mongolia[J].Environmental Science, 2013, 34(5):1895-1900.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
金姝兰, 黄益宗, 胡莹, 等.江西典型稀土矿区土壤和农作物中稀土元素含量及其健康风险评价[J].环境科学学报, 2014, 34(12):3084-3093.
Google Scholar
Jin S L, Huang Y Z, Hu Y, et al.Rare earth elements content and health risk assessment of soil and crops in typical rare earth mine area in Jiangxi Province[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(12):3084-3093.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
刘斯文, 黄园英, 韩子金, 等.离子型稀土矿山土壤生态修复研究与实践[J].环境工程, 2015, 33(11):160-165.
Google Scholar
Liu S W, Huang Y Y, Han Z J, et al.Practices of the soil ecological remediation in ion-absorbed rare earth mine[J].Environmental Engineering, 2015, 33(11):160-165.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
吴石头, 王亚平, 孙德忠, 等.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定稀土矿石中15种稀土元素——四种前处理方法的比较[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(1):12-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.01.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wu S T, Wang Y P, Sun D Z, et al.Determination of 15 rare earth elements in rare earth ores by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry:A comparison of four different pretreatment[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(1):12-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.01.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
贾双琳, 赵平, 杨刚, 等.混合酸敞开或高压密闭溶样-ICPMS测定地质样品中稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(2):186-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.02.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
Jia S L, Zhao P, Yang G, et al.Quick Determination of rare earth elements in geological samples with open acid digestion or high-pressure closed digestion by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(2):186-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2014.02.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
孙德忠, 何红蓼.封闭酸溶-等离子体质谱法分析超细粒度地质样品中42个元素[J].岩矿测试, 2007, 26(1):21-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Sun D Z, He H L. Determination of 42 elements in ultra-fine geological samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry with pressurized acid digestion[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(1):21-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
吴磊, 刘义博, 王家松, 等.高压密闭消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定锰矿石中的稀土元素前处理方法研究[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(6):637-643.
Google Scholar
Wu L, Liu Y B, Wang J S, et al.Sample treatment methods for determination of rare earth elements in manganese ore by high-pressure closed digestion-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(6):637-643.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
刘晔, 第五春荣, 柳小明, 等.密闭高温高压溶样ICP-MS测定56种国家地质标准物质中的36种痕量元素——对部分元素参考值修正和定值的探讨[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(2):221-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.02.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Liu Y, DiWu C R, Liu X M, et al.Determination of 36 trace elements in 56 chinese national standard reference materials by ICP-MS with pressurized acid-digestion[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(2):221-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.02.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Matong J M, Nyaba L, Nomngongo P N.Fractionation of trace elements in agricultural soils using ultrasound assisted sequential extraction prior to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric determination[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 154:249-257. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.123
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Sutherland R A.BCR®-701:A review of 10-years of sequential extraction analyses[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2010, 680(1-2):10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.09.016
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
中国环境监测总站.中国土壤元素背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
Google Scholar
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre.Background Value of Soil Elements in China[M].Beijing:China Enviromental Science Press, 1990.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
郑春丽, 张志彬, 刘启容, 等.稀土尾矿库区土壤中稀土形态分布规律研究[J].稀土, 2016, 37(2):73-80.
Google Scholar
Zheng C L, Zhang Z B, Liu Q R, et al.Rare earth distribution in the soil around rare earth tailings[J].Chinese Rare Earths, 2016, 37(2):73-80.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
丁友超, 刘国庆, 王晓蓉.稀土元素在土壤中的环境化学行为及其生物效应[J].农业环境科学学报, 2002, 21(6):567-569. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2002.06.027
CrossRef Google Scholar
Ding Y C, Liu G Q, Wang X R.Environmental chemical behaviors of rare earth elements in soil and their biological effects[J].Agro-Environmental Protection, 2002, 21(6):567-569. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2002.06.027
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
吴澄宇, 黄典豪, 郭中勋.江西龙南地区花岗岩风化壳中稀土元素的地球化学研究[J].地质学报, 1989, 63(4):349-362.
Google Scholar
Wu C Y, Huang D H, Guo Z X.REE geochemistry in the weathering process of granites in Longnan county, Jiangxi Province[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 1989, 63(4):349-362.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
高效江, 王玉琦, 章申, 等.赣南亚热带地球化学景观中稀土元素的分布和分异特征[J].应用基础与工程科学学报, 1997, 5(1):30-38.
Google Scholar
Gao X J, Wang Y Q, Zhang S, et al.The distribution and differentiation of rare earth elements in the geochemical landscape in a sub-tropical zone, Southern Jiangxi[J].Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 1997, 5(1):30-38.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
曹心德, 陈莹, 王晓蓉.环境条件变化对土壤中稀土元素溶解释放的影响[J].中国环境科学, 2000, 20(6):486-490. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2000.06.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Cao X D, Chen Y, Wang X R.The effects of change of environmental conditions on the release ond species transformation of rare earth elements (REEs) in soil[J].China Environmental Science, 2000, 20(6):486-490. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2000.06.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
罗才贵, 罗仙平, 苏佳, 等.离子型稀土矿山环境问题及其治理方法[J].金属矿山, 2014, 43(6):91-96.
Google Scholar
Luo C G, Luo X P, Su J, et al.Environmental problems and treatment measures in ionic-type rare earth mine[J].Metal Mine, 2014, 43(6):91-96.
Google Scholar
|





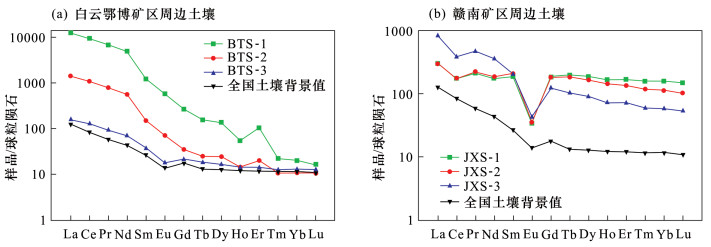

 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
