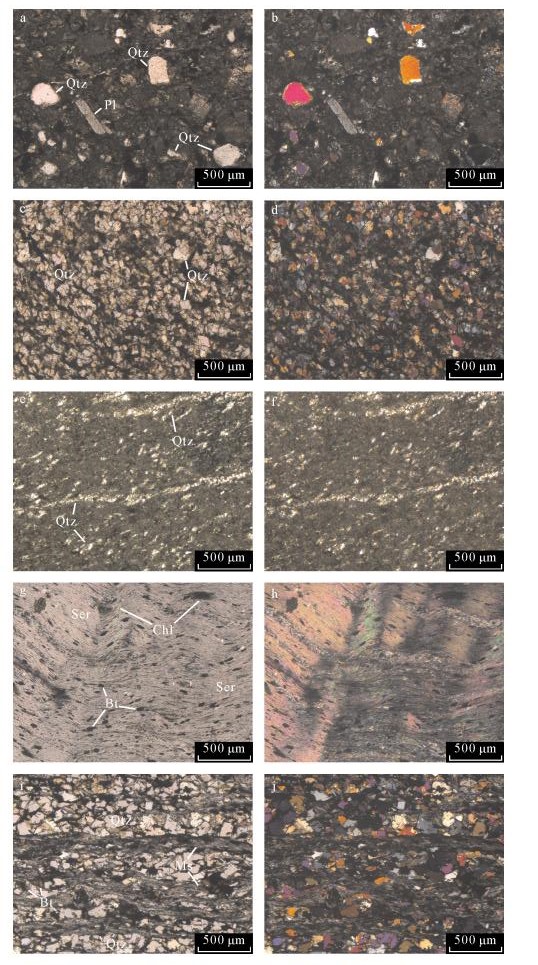
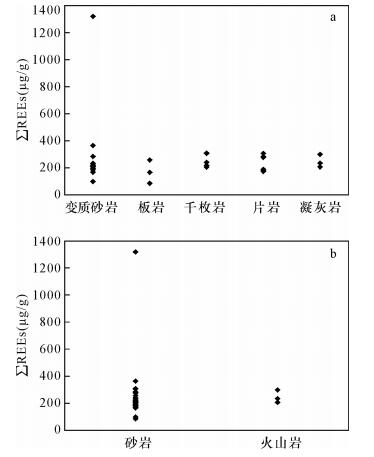
| [1] |
白鸽, 吴澄宇, 丁孝石, 等. 南岭地区离子型稀土矿床形成条件和分布规律[R]. 北京: 地质矿产部矿床地质研究所, 1989.
Google Scholar
Bai G, Wu C Y, Ding X S, et al. The Forming Condition and Distribution Law of Ionic Type Rare-Earth Ore Deposit in Nanling Region[R]. Beijing: Institute of Ore Deposit Geology, 1989.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Bern C R, Yesavage T, Foley N K.Ion-adsorption REEs in regolith of the Liberty Hill pluton, South Carolina, USA:An effect of hydrothermal alteration[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 172:29-40. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.09.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
王登红, 赵芝, 于扬, 等.我国离子吸附型稀土矿产科学研究和调查评价新进展[J].地球学报, 2017, 38(3):317-325. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.03.02
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang D H, Zhao Z, Yu Y, et al.A review of the achievements in the survey and study of ion-adsorption type REE in China[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(3):317-325. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.03.02
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Sanematsu K, Murakami H, Watanabe Y, et al.Enrichment of rare elements (REE) in granitic rocks and their weathered crusts in central and southern Laos[J].Bulletin of the Geological Survey of Japan, 2009, 60(11/12):527-558.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Foley N, Ayuso R.REE enrichment in granite-derived regolith deposits of the Southeastern United States:Prospective source rocks and accumulation processes[J].British Columbia Geological Survey Paper, 2015, 3:131-138.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Murakami H, Ishihara S.REE mineralization of weathered crust and clay sediment on granitic rocks in the Sanyo Belt, SW Japan and the Southern Jiangxi Province, China[J].Resource Geology, 2008, 58(4):373-401. doi: 10.1111/rge.2008.58.issue-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Ishihara S, Hua R, Hoshino M, et al.REE abundance and REE minerals in granitic rocks in the Nanling Range, Jiangxi Province, Southern China, and generation of the REE-rich weathered crust deposits[J].Resource Geology, 2008, 58(4):355-372. doi: 10.1111/rge.2008.58.issue-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Maulana A, Yonezu K, Watanabe K.Geochemistry of rare earth elements (REE) in the weathered crusts from the granitic rocks in Sulawesi Island, Indonesia[J].Journal of Earth Science, 2014, 25(3):460-472. doi: 10.1007/s12583-014-0449-z
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
杨岳清, 胡淙声, 罗展明.离子吸附型稀土矿床成矿地质特征及找矿方向[J].中国地质科学院院报矿床地质研究所分刊, 1981:102-118.
Google Scholar
Yang Y Q, Hu Z S, Luo Z M.Geological characteristics of mineralization of rare earth deposits of the ion-absorption type and their prospecting direction[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1981:102-118.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Bao Z W, Zhao Z H.Geochemistry of mineral with exchangeable REY in the weathering crusts of granitic rocks in South China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 33:519-535. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.03.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Sanematsu K, Watanabe Y. Characteristics and Genesis of Ion Adsorption-type Rare Earth Element Deposits[C]//Verplanck P L, Hitzman M W. Reviews in Economic Geology Vol. 18. Society of Economic Geologists. 2016: 55-79.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/299823978_Characteristics_and_Genesis_of_Ion_Adsorption-Type_Rare_Earth_Element_Deposits
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
吴澄宇.风化壳稀土成矿作用——一种不平衡过程[J].矿床地质, 1989, 8(4):85-90.
Google Scholar
Wu C Y.Rare earth mineralization in weathering crust-A nonequilibrium process[J].Mineral Deposits, 1989, 8(4):85-90.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
王登红, 陈毓川, 陈郑辉, 等.南岭地区矿产资源形势分析和找矿方向研究[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(7):882-890.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Chen Y C, Chen Z H, et al.Assessment on mineral resource in Nanling region and suggestion for further prospecting[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(7):882-890.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
王登红, 赵芝, 于扬, 等.离子吸附型稀土资源研究进展、存在问题及今后研究方向[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(5):796-802.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Zhao Z, Yu Y, et al.Progress, problems and research orientation of ion-adsorption type rare earth resources[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(5):796-802.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
王登红, 陈毓川, 王瑞江, 等.对南岭与找矿有关问题的探讨[J].矿床地质, 2013, 32(4):854-863.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Chen Y C, Wang R J.Disscussion on some problems related to prospecting breakthrough in Nanling region[J].Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(4):854-863.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
宋云华, 沈丽璞.江西某酸性火山岩风化壳中粘土矿物及其形成条件的讨论[J].矿物学报, 1982(3):207-212.
Google Scholar
Song Y H, Shen L P.Discussion of clay minerals and forming conditions in some acidic volcanic weathering crusts in Jiangxi Province[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1982(3):207-212.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
张祖海.华南风化壳离子吸附型稀土矿床[J].地质找矿论丛, 1990, 5(1):57-71.
Google Scholar
Zhang Z H.A study on weathering crust ion adsorption type REEdeposits, South China[J]. Contribution to Geology and Mineral Resource Research, 1990, 5(1):57-71.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
华仁民, 张文兰, 顾晟彦, 等.南岭稀土花岗岩、钨锡花岗岩及其成矿作用的对比[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2321-2328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
Hua R M, Zhang W L, Gu S Y, et al.Comparison between REE granite and W-Sn granite in the Nanling region, South China, and their mineralizations[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(10):2321-2328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
赵芝, 王登红, 陈振宇, 等.南岭东段与稀土矿有关岩浆岩的成矿专属性特征[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(2):255-263.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z, Wang D H, Chen Z Y, et al.Metallogenic specialization of rare earth mineralized igneous rocks in the Eastern Nanling Region[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2014, 38(2):255-263.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
刘邦秀, 刘春根, 邱永泉.江西南部鹤仔片麻状花岗岩类Pb-Pb同位素年龄及地质意义[J].火山地质与矿产, 2001, 22(4):264-268.
Google Scholar
Liu B X, Liu C G, Qiu Y Q.The Pb-Pb isotopic ages and geologic significance of gneissic granite in Hezi, Jiangxi[J].Volcanology & Mineral Resources, 2001, 22(4):264-268.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
王丽娟, 于津海, O'Reilly S Y, 等.华夏南部可能存在Grenville期造山作用:来自基底变质岩中锆石U-Pb定年及Lu-Hf同位素信息[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(14):1680-1692. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.14.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang L J, Yu J H, O'Reilly S Y, et al.Grenvillian orogeny in the Southern Cathaysia Block:Constraints from U-Pb ages and Lu-Hf isotopes in zircon from metamorphic basement[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2008, 53(14):1680-1692. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.14.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
于津海, 王丽娟, O'Reilly S Y, 等.赣南存在古元古代基底:来自上犹陡水煌斑岩中捕虏锆石的U-Pb-Hf同位素证据[J].科学通报, 2009, 54(7):898-905.
Google Scholar
Yu J H, Wang L J, O'Reilly S Y, et al.Paleoproterozoic basement beneath the Southern Jiangxi Province:Evidence from U-Pb ages and Lu-Hf isotopes in zircons from the Doushui lamprophyre[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(7):898-905.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
靳松, 张利, 钟增球, 等.浙闽地区华夏地块新元古代变沉积岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2008, 33(6):764-774.
Google Scholar
Jin S, Zhang L, Zhong Z Q, et al.Geochemical characteristics and geological implications for the Neoproterozoic meta-sedimentary rocks of the Cathaysia block in Zhejiang and Fujian Province[J].Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008, 33(6):764-774.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
王仁民, 贺高品, 陈珍珍, 等.变质岩原岩图解判别法[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987:1-51.
Google Scholar
Wang R M, He G P, Chen Z Z, et al.Graphic Method for Protolith Metamorphic Rocks[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1987:1-51.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Shaw D M.The origin of the Apsley gneiss, Ontario[J].Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1972, 9:18-35. doi: 10.1139/e72-002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
赵芝, 王登红, 刘新星, 等.广西花山岩体不同风化阶段稀土元素特征及其影响因素[J].稀土, 2015, 36(3):14-20.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z, Wang D H, Liu X X, et al.Geochemical features of rare earth elements in different weathering stage of the Guangxi Huashan granite and its influence factors[J].Chinese Rare Earths, 2015, 36(3):14-20.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
池汝安, 田君, 罗仙平, 等.风化淋积型稀土矿的基础研究[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2012, 3(4):1-13.
Google Scholar
Chi R A, Tian J, Luo X P, et al.The basic research on the weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth ores[J].Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2012, 3(4):1-13.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
宋云华, 沈丽璞, 王贤觉.某些岩石风化壳中稀土元素的初步探讨[J].科学通报, 1987, 32(9):695-698.
Google Scholar
Song Y H, Shen L P, Wang X J.Preliminary discussion of rare earth elements in some weathering crusts[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 1987, 32(9):695-698.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
包志伟.华南花岗岩风化壳稀土元素地球化学研究[J].地球化学, 1992(2):166-174.
Google Scholar
Bao Z W.A geochemical study of the granitoid weathering crust in Southeast China[J].Geochimica, 1992(2):166-174.
Google Scholar
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: