| [1] |
Sloan Jr E D, Koh C.Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases (The Third Edition)[M].New York:CRC Press, 2007:1-2.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Udachin K A, Ripmeester J A.A complex clathrate hydrate structure showing bimodal guest hydration[J].Nature, 1999, 397:420-423. doi: 10.1038/17097
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Sloan Jr E D, Koh C.Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases (The Second Edition)[M].New York:CRC Press, 1998:223-224.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Kvenvolden K A, Lorenson T D.The global occurrence of natural gas hydrates[J].American Geophysical Union, 2001, 124:3-18.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Milkov A V.Global estimates of hydrate-bound gas in marine sediments:How much is really out there?[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2004, 66(3):183-197.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Song Y, Yang L, Zhao J, et al.The status of natural gas hydrate research in China:A review[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 31:778-791. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.12.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
何勇, 苏正, 吴能友.海底天然气水合物稳定带厚度的影响因素[J].海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(5):43-47.
Google Scholar
He Y, Su Z, Wu N Y.Factors influencing the thickness of gas hydrate stability zone in marine sediments[J].Marine Geology Frontiers, 2012, 28(5):43-47.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Sun C Y, Li W Z, Yang X, et al.Progress in research of gas hydrate[J].Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2011, 19(1):151-162. doi: 10.1016/S1004-9541(09)60192-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
宋海斌, 耿建华, Wang How-Kin, 等.南海北部东沙海域天然气水合物的初步研究[J].地球物理学报, 2001, 44(5):687-695.
Google Scholar
Song H B, Geng J H, Wang H K, et al.A preliminary study of gas hydrates in Dongsha region north of South China Sea[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2001, 44(5):687-695.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Lu S M.A global survey of gas hydrate development and reserves:Specifically in the marine field[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 41(C):884-900.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Nisbet E G, Piper D J W.Giant submarine landslides[J].Nature, 1998, 392(6674):329-330. doi: 10.1038/32765
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Bains S, Corfield R M, Norris R D.Mechanisms of climate warming at the end of the Paleocene[J].Science, 1999, 285(5428):724-727. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5428.724
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Matsumoto R, Uchida T, Waseda A, et al. Occurrence, Structure and Composition of Natural Gas Hydrate Recovered from the Blake Ridge, Northwest Atlantic[R]. Proceedings of Ocean Drill Program Science Results, 2000: 13-28.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025322707001387
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Kvenvolden K A, Lorenson T D. The Global Occurrence of Natural Gas Hydrate[R]//Natural Gas Hydrates: Occurrence, Distribution, and Detection[J]. 2001: 3-18.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/book/10.1029/GM124
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
金春爽, 汪集旸, 张光学.南海天然气水合物稳定带的影响因素[J].矿床地质, 2005, 24(4):388-397.
Google Scholar
Jin C S, Wang J Y, Zhang G X.Factors affecting natural gas hydrate stability zone in the South China Sea[J].Mineral Deposits, 2005, 24(4):388-397.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
王宏斌, 梁劲, 龚跃华, 等.基于天然气水合物地震数据计算南海北部陆坡海底热流[J].现代地质, 2005, 19(1):67-73.
Google Scholar
Wang H B, Liang J, Gong Y H, et al.Estimation of the heat flow in the northern of the South China Sea based on the seismic data of gas hydrate[J].Geoscience, 2005, 19(1):67-73.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
张金华, 魏伟, 张吝文.海底天然气水合物相平衡及稳定带的影响分析[J].化学工程与装备, 2011(1):39-42.
Google Scholar
Zhang J H, Wei W, Zhang L W.Analysis of phase equilibrium and stability zone of gas hydrate in submarine[J].Chemical Engineering & Equipment, 2011(1):39-42.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Booth J S, Winters W J, Dillon W P, et al.Major Occurrences and Reservoir Concepts of Marine Clathrate Hydrates:Implications of Field Evidence[M].London:Woods Hole Coastal and Marine Science Center, 1998:113-127.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
许威, 邱楠生, 孙长宇, 等.不同因素对天然气水合物稳定带厚度的影响[J].天然气地球科学, 2010, 21(3):528-534.
Google Scholar
Xu W, Qiu N S, Sun C Y, et al.Different factors on the thickness of gas hydrate stability zone[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2010, 21(3):528-534.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Milkov A V, Sassen R.Thickness of the gas hydrate stability zone, Gulf of Mexico continental slope[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(9):981-991. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(00)00051-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Milkov A V, Sassen R.Economic geology of offshore gas hydrate accumulations and provinces[J].Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2002, 19(1):1-11.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
杨顶辉, Xu Wenyue.盐度对甲烷气水合物系统的影响[J].中国科学(D辑), 2007, 37(10):1370-1381.
Google Scholar
Yang D H, Xu W Y.Effects of salinity on methane hydrate system[J].Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2007, 37(10):1370-1381.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Handa Y P.Effect of hydrostatic pressure and salinity on the stability of gas hydrates[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1990, 94:2652-2657. doi: 10.1021/j100369a077
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Sylva T Y, Kinoshita C K, Masutani S M.Inhibiting effects of transition metal salts on methane hydrate stability[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 155:10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2016.06.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Sun S C, Kong Y Y, Zhang Y, et al.Phase equilibrium of methane hydrate in silica sand containing chloride salt solution[J].The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2015, 90:116-121. doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2015.06.030
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Villard M.Sur les hydrates de méthane et d'éthylène[J].Comptes Rendus, 1888, 107:257.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Deaton W M, Frost Jr E M. Gas Hydrates and Their Relation to the Operation of Natural-gas Pipe Lines[R]. Bureau of Mines, Amarillo, TX (USA): Helium Research Center, 1946.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
de Roo J L, Peters C J, Lichtenthaler R N, et al.Occurrence of methane hydrate in saturated and unsaturated solutions of sodium chloride and water in dependence of temperature and pressure[J].AIChE Journal, 1983, 29(4):651-657. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Millero F J, Feistel R, Wright D G, et al.The com-position of standard seawater and the definition of the reference-composition salinity scale[J].Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ:Oceanographic Research Papers, 2008, 55(1):50-72. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2007.10.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Aparicio-González A, Duarte C M, Tovar-Sánchez A.Trace metals in deep ocean waters:A review[J].Journal of Marine Systems, 2012, 100:26-33.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Ross M J, Toczylkin L S.Hydrate dissociation pressures for methane or ethane in the presence of aqueous solutions of triethylene glycol[J].Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 1992, 37(4):488-491. doi: 10.1021/je00008a026
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Kang S P, Chun M K, Lee H.Phase equilibria of methane and carbon dioxide hydrates in the aqueous MgCl2 solutions[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1998, 147(1):229-238.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Jager M D, Sloan E D.The effect of pressure on methane hydration in pure water and sodium chloride solutions[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2001, 185(1):89-99.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
van der Waals J H, Platteeuw J C. Clathrate Solutions[M]//Prigogine Ⅰ: Advances in Chemical Physics Ⅱ. New York, 1959.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Duan Z, Li D, Chen Y, et al.The influence of temper-ature, pressure, salinity and capillary force on the formation of methane hydrate[J].Geoscience Frontiers, 2011, 2(2):125-135. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2011.03.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
Tishchenko P, Hensen C, Wallmann K, et al.Calculation of the stability and solubility of methane hydrate in seawater[J].Chemical Geology, 2005, 219(1):37-52.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
Chin H Y, Lee B S, Chen Y P, et al.Prediction of phase equilibrium of methane hydrates in the presence of ionic liquids[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(47):16985-16992.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
Parrish W R, Prausnitz J M.Dissociation pressures of gas hydrates formed by gas mixtures[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1972, 11(1):26-35.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
Rashid S, Fayazi A, Harimi B, et al.Evolving a robust approach for accurate prediction of methane hydrate formation temperature in the presence of salt inhibitor[J].Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering, 2014, 18(2):194-204.
Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
Ng H J, Robinson D B.Hydrate formation in systems containing methane, ethane, propane, carbon dioxide or hydrogen sulfide in the presence of methanol[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1985, 21(1-2):145-155. doi: 10.1016/0378-3812(85)90065-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
Lee S Y, Holder G D.Model for gas hydrate equilibria using a variable reference chemical potential:Part 1[J].AIChE Journal, 2002, 48(1):161-167. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
Englezos P, Bishnoi P R.Prediction of gas hydrate formation conditions in aqueous electrolyte solutions[J].AIChE Journal, 1988, 34(10):1718-1721. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
Shabani M M, Rashtchian D, Ghotbi C, et al.Prediction of hydrate formation for the systems containing single and mixed electrolyte solutions[J].Iranian Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, 2007, 26(1):35-45.
Google Scholar
|
| [44] |
Javanmardi J, Moshfeghian M, Maddox R N.Simple method for predicting gas-hydrate-forming conditions in aqueous mixed-electrolyte solutions[J].Energy & Fuels, 1998, 12(2):219-222.
Google Scholar
|
| [45] |
Javanmardi J, Moshfeghian M.A new approach for prediction of gas hydrate formation conditions in aqueous electrolyte solutions[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2000, 168(2):135-148. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3812(99)00322-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [46] |
孙长宇, 黄强, 陈光进.气体水合物形成的热力学与动力学研究进展[J].化工学报, 2006, 57(5):1031-1039.
Google Scholar
Sun C Y, Huang Q, Chen G J.Progress of thermodynamics and kinetics of gas hydrate formation[J].Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2006, 57(5):1031-1039.
Google Scholar
|
| [47] |
Palermo T, Arla D, Borregales M, et al. Study of the Agglomeration between Hydrate Particles in Oil Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)[C]//Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Gas Hydrates. 2005: 12-16.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009250908003539
Google Scholar
|
| [48] |
Dalmazzone D, Hamed N, Dalmazzone C.DSC measure-ments and modelling of the kinetics of methane hydrate formation in water-in-oil emulsion[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(9):2020-2026. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2009.01.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [49] |
Thatai S, Khurana P, Prasad S, et al.Plasmonic detection of Cd2+ ions using surface-enhanced Raman scattering active core-shell nanocomposite[J].Talanta, 2015, 134:568-575. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.11.024
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [50] |
Bonales L J, Muñoz-Iglesias V, Santamaría-Pérez D, et al.Quantitative Raman spectroscopy as a tool to study the kinetics and formation mechanism of carbonates[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2013, 116:26-30. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.06.121
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [51] |
Sum A K, Burruss R C, Sloan E D.Measurement of clathrate hydrates via Raman spectroscopy[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1997, 101(38):7371-7377. doi: 10.1021/jp970768e
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [52] |
Subramanian S, Sloan Jr E D.Molecular measurements of methane hydrate formation[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1999, 158-160:813-820. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3812(99)00134-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [53] |
Chazallon B, Focsa C, Charlou J L, et al.A comparative Raman spectroscopic study of natural gas hydrates collected at different geological sites[J].Chemical Geology, 2007, 244(1):175-185.
Google Scholar
|
| [54] |
Uchida A, Jagendorf A T, Hibino T, et al.Effects of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide on both salt and heat stress tolerance in rice[J].Plant Science, 2002, 163(3):515-523. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00159-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [55] |
陈勇, 周瑶琪.天然流体包裹体中甲烷水合物生成条件原位变温拉曼光谱研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2007, 27(8):1547-1550.
Google Scholar
Chen Y, Zhou Y Q.In situ temperature-dependent Raman spectroscopic on methane hydrate formation in natural fluid inclusion[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2007, 27(8):1547-1550.
Google Scholar
|
| [56] |
吕万军, I-Ming Chou, Robert C.Burruss, 等.拉曼光谱原位观测水合物形成后的饱和甲烷浓度[J].地球化学, 2005, 34(2):187-192.
Google Scholar
Lü W J, Chou I M, Burruss R C, et al.In situ observation of variation of methane concentration in water during the growth of hydrate using Raman spectroscopy[J].Geochemica, 2005, 34(2):187-192.
Google Scholar
|
| [57] |
Hesse R.Pore-water anomalies in gas hydrate-bearing sediments of the deeper continental margins:Facts and problems[J].Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry, 1990, 8(1):117-138.
Google Scholar
|
| [58] |
马燕. 盐溶液体系中天然气水合物稳定性的研究[D]. 淄博: 山东理工大学, 2011.
Google Scholar
Ma Y. Study on the Stability of Natural Gas Hydrates in the Salt Solution System[D]. Zibo: Shandong University of Technology, 2011.
Google Scholar
|
| [59] |
Maekawa T.Equilibrium conditions for gas hydrates of methane and ethane mixtures in pure water and sodium chloride solution[J].Geochemical Journal, 2001, 35(1):59-66. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.35.59
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [60] |
Lu H, Matsumoto R.Experimental studies on the possible influences of composition changes of pore water on the stability conditions of methane hydrate in marine sediments[J].Marine Chemistry, 2005, 93(2):149-157.
Google Scholar
|
| [61] |
Kharrat M, Dalmazzone D.Experimental determination of stability conditions of methane hydrate in aqueous calcium chloride solutions using high pressure differential scanning calorimetry[J].The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2003, 35(9):1489-1505. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9614(03)00121-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [62] |
Atik Z, Windmeier C, Oellrich L R.Experimental gas hydrate dissociation pressures for pure methane in aqueous solutions of MgCl2 and CaCl2 and for a (methane+ethane) gas mixture in an aqueous solution of (NaCl+MgCl2)[J].Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2006, 51(5):1862-1867.
Google Scholar
|
| [63] |
Mohammadi A H, Afzal W, Richon D.Gas hydrates of methane, ethane, propane, and carbon dioxide in the presence of single NaCl, KCl, and CaCl2 aqueous solutions:Experimental measurements and predictions of dissociation conditions[J].The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2008, 40(12):1693-1697. doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2008.06.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [64] |
Mohammadi A H, Kraouti I, Richon D.Methane hydrate phase equilibrium in the presence of NaBr, KBr, CaBr2, K2CO3, and MgCl2 aqueous solutions:Experimental measurements and predictions of dissociation conditions[J].The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2009, 41(6):779-782. doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2009.01.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [65] |
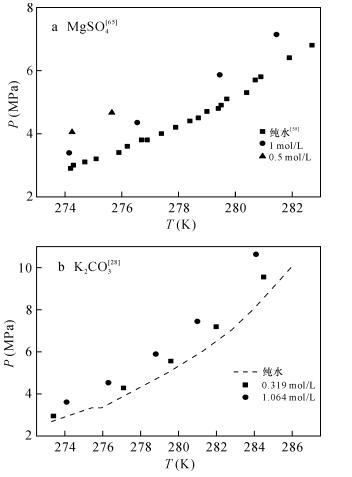
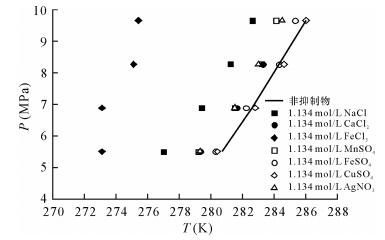
Lu H, Matsumoto R, Tsuji Y, et al.Anion plays a more important role than cation in affecting gas hydrate stability in electrolyte solution?-A recognition from experimental results[J].Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2001, 178(1):225-232.
Google Scholar
|
| [66] |
宋永臣, 杨明军, 刘瑜, 等.离子对甲烷水合物相平衡的影响[J].化工学报, 2009(6):1362-1366.
Google Scholar
Song Y C, Yang M J, Liu Y, et al.Influence of ions on phase equilibrium of methane hydrate[J].Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2009(6):1362-1366.
Google Scholar
|
| [67] |
Berecz E, Balla-Achs M.Gas Hydrates[M].New York:Elsevier Science Publishing Company, 1983.
Google Scholar
|
| [68] |
Liu C L, Ye Y G, Sun S C, et al.Experimental studies on the P-T stability conditions and influencing factors of gas hydrate in different systems[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2013, 56(4):594-600. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4564-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [69] |
Dholabhai P D, Englezos P, Kalogerakis N, et al.Equilibrium conditions for methane hydrate formation in aqueous mixed electrolyte solutions[J].The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1991, 69(3):800-805. doi: 10.1002/cjce.v69:3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [70] |
刘伟, 金翔龙, 初凤友, 等.海底天然气水合物相平衡的影响因素[J].海洋地质前沿, 2011, 27(5):16-23.
Google Scholar
Liu W, Jin X L, Chu F Y, et al.Research on influencing factors of gas hydrate phase equilibrium in marine sediments[J].Marine Geology Frontiers, 2011, 27(5):16-23.
Google Scholar
|
| [71] |
Pieroen A P.Gas hydrates-approximate relations between heat of formation, composition and equilibrium temperature lowering by "inhibitors"[J].Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 1955, 74(8):995-1002.
Google Scholar
|
| [72] |
Dickens G R, Quinby-Hunt M S.Methane hydrate stability in pore water:A simple theoretical approach for geophysical applications[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1997, 102(B1):773-783. doi: 10.1029/96JB02941
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [73] |
黄子卿.电解质溶液理论导论[M].北京:科学出版社, 1983:49-51.
Google Scholar
Huang Z Q.Introduction of Theoretical Electrolyte Solution[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1983:49-51.
Google Scholar
|
| [74] |
Sabil K M, Duarte A R C, Zevenbergen J, et al.Kinetic of formation for single carbon dioxide and mixed carbon dioxide and tetrahydrofuran hydrates in water and sodium chloride aqueous solution[J].International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2010, 4(5):798-805. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.05.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: