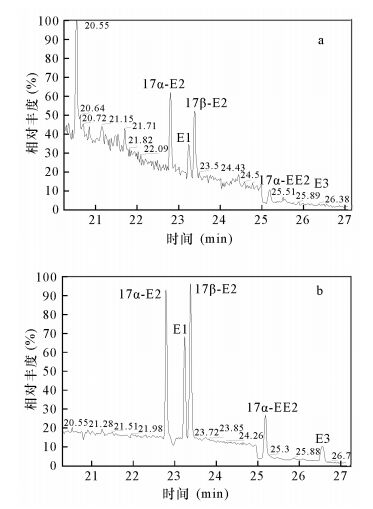
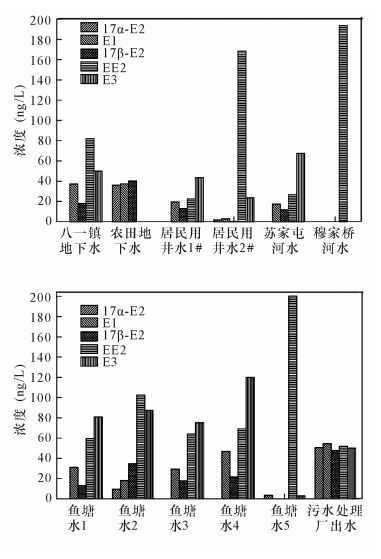
| [1] |
Chowdhury R R, Charpentier P A, Ray M B.Photode-gradation of 17β-estradiol in aquatic solution under solar irradiation:Kinetics and infiuencing water parameters[J].Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A:Chemistry, 2011, 219:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2011.01.019
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Chambers K B, Casey F X, Hakk H, et al.Potential bioactivity and association of 17β-estradiol with the dissolved and colloidal fractions of manure and soil[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 494-495:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.121
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Zheng W, Zou Y, Li X, et al.Fate of estrogen conjugate 17α-estradiol-3-sulfate in dairy wastewater:Comparison of aerobic and anaerobic degradation and metabolite formation[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 258-259:109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.04.038
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Liu Z H, Lu G N, Yin H, et al.Removal of natural estro-gens and their conjugates in municipal wastewater treatment plants:A critical review[J].Environment Science & Technology, 2015, 49:5288-5300.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
都韶婷, 金崇伟, 刘越.水体SEs污染现状研究进展[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(9):3358-3365.
Google Scholar
Du S T, Jin C W, Liu Y.A review on current situations of steroid estrogen in the water system[J].Environmental Science, 2013, 34(9):3358-3365.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Sun W L, Zhou K.Adsorption of 17β-estradiol by multi-walled carbon nanotubes in natural waters with or without aquatic colloids[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 258:185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.087
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
D'Alessio M, Vasudevan D, Lichwa J, et al.Fate and transport of selected estrogen compounds in Hawaii soils:Effect of soil type and macropores[J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2014, 166:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2014.07.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Combalbert S, Hernandez-raquet G.Occurrence, fate and biodegradation of estrogens in sewage and manure[J].Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 86(6):1671-1692. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2547-x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Jiang J Q, Yin Q, Zhou J L, et al.Occurrence and treatment trials of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in wastewaters[J].Chemosphere, 2005, 61(4):544-550. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.029
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Shrestha S L, Casey F X, Hakk H, et al.Fate and transformation of an estrogen conjugate and its metabolites in agricultural soils[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46:11047-11053.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Bai X L, Shrestha S L, Francis X M, et al.Modeling coupled sorption and transformation of 17β-estradiol-17-sulfate in soil-water systems[J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2014, 168:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2014.09.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Lee J, Bartelthunt S L, Li Y, et al.Effect of 17β-estradiol on stability and mobility of TiO2 rutile nanoparticles[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 511:195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.054
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Goeppert N, Dror I, Berkowitz B.Fate and transport of free and conjugated estrogens during soil passage[J].Environmental Pollution, 2015, 206:80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.06.024
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Singh R, Cabrera M L, Radcliffe D E, et al.Laccase me-diated transformation of 17β-estradiol in soil[J].Environmental Pollution, 2015, 197:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.11.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Postigo C.Synthetic organic compounds and their trans-formation products in groundwater:Occurrence, fate and mitigation[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 503-504:32-47. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.019
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Schuh M C, Casey F X, Hakk H, et al.Effects of field-manure applications on stratified 17β-estradiol concentrations[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192:748-752. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.080
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Lucci P, Núñ nez O, Galceran M T.Solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of natural and synthetic estrogens from aqueous samples[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(30):4828-4833. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.02.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Zheng M, Wang L, Bi Y, et al.Improved method for analyzing the degradation of estrogens in water by solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(4):693-698. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60439-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Fredj S B, Nobbs J, Tizaoui C, et al.Removal of estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2), and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) from wastewater by liquid-liquid extraction[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 262:417-426. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Naing N N, Li S F Y, Lee H K.Evaluation of graphene-based sorbent in the determination of polar environmental contaminants in water by micro-solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1427:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.12.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Wang J, Chen Z, Li Z, et al.Magnetic nanoparticles based dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction as a novel technique for the determination of estrogens in pork samples[J].Food Chemistry, 2016, 204:135-140. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.016
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Luo S, Fang L, Wang X, et al.Determination of octyl-phenol and nonylphenol in aqueous sample using simultaneous derivatization and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217(43):6762-6768. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2010.06.030
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Wang P, Xiao Y, Liu W, et al.Vortex-assisted hollow fibre liquid-phase microextraction technique combined with high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection for the determination of oestrogens in milk samples[J].Food Chemistry, 2015, 172:385-390. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.092
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
González A, Avivar J, Cerdà V.Estrogens determination in wastewater samples by automatic in-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior silylation and gas chromatography[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1413:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.08.031
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Manickum T, John W.The current preference for the immuno-analytical ELISA method for quantitation of steroid hormones (endocrine disruptor compounds) in wastewater in South Africa[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2015, 407(17):4949-4970. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-8546-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
王硕, 陈双, 方国臻, 等.分子印迹技术在环境雌激素检测中的应用[J].食品与生物技术学报, 2008, 26(6):99-104.
Google Scholar
Wang S, Chen S, Fang G Z, et al.Determination of environmental estrogens by molecular imprinting technique[J].Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2008, 26(6):99-104:99-104.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Bai X, Casey F X, Hakk H, et al.Sorption and degra-dation of 17β-estradiol-17-sulfate in sterilized soil-water systems[J].Chemosphere, 2015, 119:1322-1328. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.016
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Kumar V, Johnson A C, Nakada N, et al.De-conjugation behavior of conjugated estrogens in the raw sewage, activated sludge and river water[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 227-228:49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.078
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Ronan J M, Mchugh B.A sensitive liquid chromatogra-phy/tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of natural and synthetic steroid estrogens in seawater and marine biota, with a focus on proposed Water Framework Directive Environmental Quality Standards[J].Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2013, 27:738-746. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6505
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Atapattu S N, Rosenfeld J M.Solid phase analytical derivatization of anthropogenic and natural phenolic estrogen mimics with pentafluoropyridine for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218:9135-9141. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.10.060
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
余方, 潘学军, 王彬, 等.固相萃取-羟基衍生化-气相色谱/质谱联用测定滇池水体中酚类内分泌干扰物[J].环境化学, 2010, 29(4):744-748.
Google Scholar
Yu F, Pan X J, Wang B, et al.Determination of phenols in surface water of dianchi lake by solid extraction-hydroxyl derivatization-GC-MS[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2010, 29(4):744-748.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
廖涛, 吴晓翠, 王少华, 等.固相萃取-气相色谱/质谱联用法同时检测水体中9种环境雌激素[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(3):422-426.
Google Scholar
Liao T, Wu X C, Wang S H, et al.Simultaneous detection of nine kinds of estrogens in water by solid phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(3):422-426.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
黄成, 姜理英, 陈建孟, 等.固相萃取-衍生化气相色谱/质谱法测定制药厂污水中的环境雌激素[J].色谱, 2008, 26(5):618-621.
Google Scholar
Huang C, Jiang L Y, Chen J M, et al.Determination of environmental estrogens in pharmacy wastewater using solid-phase extraction-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry with derivatization[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2008, 26(5):618-621.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Quintana J B, Carpinteiro J, Rodríguez I, et al.Deter-mination of natural and synthetic estrogens in water by gas chromatography with mass spectrometric detection[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1024:177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2003.10.074
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Nie Y F, Qiang Z M, Zhang H Q, et al.Determination of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the liquid and solid phases of activated sludge by solid phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2009, 1216(42):7071-7080. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.08.064
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
Liu R, Zhou J L, Wilding A.Simultaneous determination of endocrine disrupting phenolic compounds and steroids in water by solid-phase extraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1022(1):179-189.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
黄斌, 潘学军, 万幸, 等.固相萃取衍生化气相色谱/质谱测定水中类固醇类环境内分泌干扰物[J].分析化学, 2011, 39(4):449-454.
Google Scholar
Huang B, Pan X J, Wan X, et al.Simultaneous determination of steroid endocrine disrupting chemicals in water by solid phase extraction-derivatization-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 39(4):449-454.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
张宏, 毛炯, 孙成均, 等.气相色谱-质谱法测定尿及河底泥中的环境雌激素[J].色谱, 2003, 21(5):451-455.
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Mao J, Sun C J, et al.Determination of environmental estrogens in urine and bed mud by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2003, 21(5):451-455.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
Delaune P B, Jr M P.17β-estradiol in runoff as affected by various poultry litter application strategies[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 444:26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.054
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
Zhang H, Shi J, Liu X, et al.Occurrence and removal of free estrogens, conjugated estrogens, and bisphenol A in manure treatment facilities in East China[J].Water Research, 2014, 58:248-257. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.074
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
Bevacqua C E, Rice C P, Torrents A, et al.Steroid hor-mones in biosolids and poultry litter:A comparison of potential environmental inputs[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409:2120-2126. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.02.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
Caron E, Farenhorst A, Mcqueen R, et al.Mineralization of 17β-estradiol in 36 surface soils from Alberta, Canada[J].Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2010, 139:534-545. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2010.09.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
Lee B, Kullman S W, Yost E E, et al.Predicting charac-teristics of rainfall driven estrogen runoff and transport from swine AFO spray fields[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 532:571-580. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.051
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





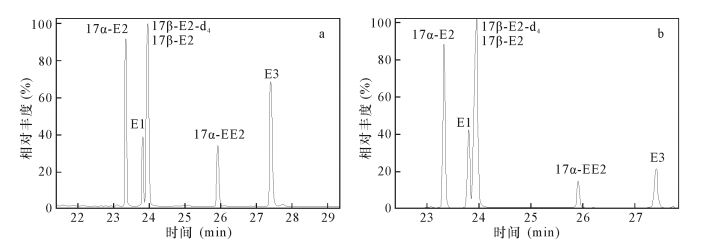

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: