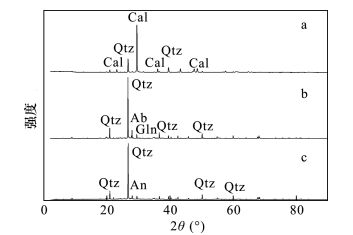
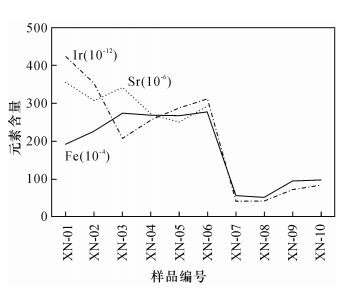
| [1] |
Liang X Q, Wen S N, Yang D S, et al.Dinosaur eggs and dinosaur egg-bearing deposits (Upper Cretaceous) of Henan Province, China:Occurrences, palaeoenvi-ronments, taphonomy and preservation[J].Progress in Natural Science:Materials International, 2009, 19(11):1587-1601. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2009.06.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Paik I S, Huh M, Kim H J.Dinosaur egg-bearing deposits(Upper Cretaceous) of Boseong, Korea:Occurrence, palaeoenvironments, taphonomy, and preservation[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2004, 205(1-2):155-168. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2003.12.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Paik I S, Kim H J, Huh M.Dinosaur egg deposits in the Cretaceous Gyeongsang Supergroup, Korea:Diversity and paleobiological implications[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 56(3):135-146.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Kim C B, Al-Aasm I S, Ghazban F, et al.Stable isotopic composition of dinosaur eggshells and pedogenic carbonates in the Upper Cretaceous Seonso Formation, South Korea:Paleoenvironmental and diagenetic implications[J].Cretaceous Research, 2009, 30(1):93-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2008.05.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Montanari S, Higgins P, Norell M A.Dinosaur eggshell and tooth enamel geochemistry as an indicator of Mongolian Late Cretaceous paleoenvironments[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 370(4):158-166.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Riera V, Anadón P, Oms O, et al.Dinosaur eggshell isotopegeochemistry as tools of palaeoenvironmental reconstruction for the Upper Cretaceous from the Tremp Formation (Southern Pyrenees)[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2013, 294(3):356-370.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Sellés A G, Bravo A M, Delclòs X, et al.Dinosaur eggs in the Upper Cretaceous of the Coll De Nargó Area, Lleida Province, South-Central Pyrenees, Spain:Oodiversity, biostratigraphy and their implications[J].Cretaceous Research, 2013, 40:10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2012.05.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Tanaka K, Zelenitsky D K, Saegusa H, et al.Dinosaur eggshell assemblage from Japan reveals unknown diversity of small theropods[J].Cretaceous Research, 2016, 57:350-363. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2015.06.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
赵资奎.河南内乡新的恐龙蛋类型和恐龙脚印化石的发现及其意义[J].古脊椎动物学报, 1979, 17(4):304-309.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z K.Discovery of the dinosaurian eggs and footprint from Neixiang County, Henan Province[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1979, 17(4):304-309.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Sarkar A, Bhattacharya S K, Mohabey D M.Stable-isotope analyses of dinosaur eggshells:Paleoenvironmental implications[J].Geology, 1991, 19(11):1068-1071. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<1068:SIAODE>2.3.CO;2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
方晓思, 卢立伍, 蒋严根, 等.浙江天台盆地蛋化石与恐龙的绝灭[J].地质通报, 2003, 22(7):512-520.
Google Scholar
Fang X S, Lu L W, Jiang Y G, et al.Cretaceous fossil eggs from the Tiantai basin of Zhejiang, with a discussion on the extinction of dinosaurs[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2003, 22(7):512-520.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Gottfried M D, O'connor P M, Jackson F D, et al.Dinosaureggshell from the Red Sandstone Group of Tanzania[J].Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 2004, 24(2):494-497. doi: 10.1671/0272-4634(2004)024[0494:DEFTRS]2.0.CO;2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Zhao Z K, Mao X Y, Chai Z F, et al.Geochemical environmentalchanges and dinosaur extinction during the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K/T) Transition in the Nanxiong Basin, South China:Evidence from dinosaur eggshells[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(5):806-815.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Zelenitsky D K, Therrien F, Tanaka K, et al.Dinosaur eggshells from the Santonian Milk River Formation of Alberta, Canada[J].Cretaceous Research, 2017, 74:181-187. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2017.02.016
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
赵资奎, 蔣元凯.山东莱阳恐龙蛋化石的显微结构研究[J].中国科学(A辑), 1974, 17(1):63-72.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z K, Jiang Y K.The microstructrue of dinosaur eggs from Laiyang county, Shandong Province[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 1974, 17(1):63-72.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
刘金远, 赵资奎.山东莱阳晚白垩世恐龙蛋化石——新类型[J].古脊椎动物学报, 2004, 42(2):166-170.
Google Scholar
Liu J Y, Zhao Z K.A new oospecies of the dinosaur eggs (DICTYOOLITHUS) from Laiyang, Shandong Province[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2004, 42(2):166-170.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
王强, 赵资奎, 汪筱林, 等.浙江天台晚白垩世巨型长形蛋科一新属及巨型长形蛋科的分类订正[J].古生物学报, 2010, 49(1):73-86.
Google Scholar
Wang Q, Zhao Z K, Wang X L, et al.A new oogenus of Macroelongatoolithid eggs from the Upper Cretaceous Chichengshan Formation of the Tiantai Basin, Zhejiang Province and a revision of the Macroelongatoolithids[J].Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2010, 49(1):73-86.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
张蜀康.中国白垩纪蜂窝蛋化石的分类订正[J].古脊椎动物学报, 2010, 48(3):203-219.
Google Scholar
Zhang S K.A parataxonomic revision of the Cretaceous Faveoloolithid eggs of China[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2010, 48(3):203-219.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
刘金远, 王强, 赵资奎, 等.辽宁昌图上白垩统泉头组恐龙蛋化石的分类订正[J].古脊椎动物学报, 2013, 51(4):278-288.
Google Scholar
Liu J Y, Wang Q, Zhao Z K, et al.A parataxonomic revision of spheroolithid eggs from the Upper Cretaceous Quantou Formation in Changtu, Liaoning[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2013, 51(4):278-288.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
王强, 赵资奎, 汪筱林, 等.浙江天台盆地晚白垩世恐龙蛋新类型(英文)[J].古脊椎动物学报, 2011, 49(4):446-449.
Google Scholar
Wang Q, Zhao Z K, Wang X L, et al.New ootypes of dinosaur eggs from the Late Cretaceous in Tiantai Basin, Zhejiang Province, China[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2011, 49(4):446-449.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Xie J F, Zhang S K, Jin X S, et al.A new type of dinosaur eggsfrom Early Cretaceous of Gansu Province, China[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2016, 54(1):79-88.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
张蜀康, 王强.记新疆吐鲁番盆地椭圆形蛋类一新种[J].古脊椎动物学报, 2010, 48(1):71-75.
Google Scholar
Zhang S K, Wang Q.A new oospecies of Ovaloolithids from Turpan Basin in Xinjiang, China[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 2010, 48(1):71-75.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
杨钟健.广东南雄、始兴, 江西赣州的蛋化石[J].古脊椎动物学报, 1965, 9(2):141-179.
Google Scholar
Yang Z J.Fossil eggs from Nanhsiung, Kwangtung and Kanchou, Kiangsi[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1965, 9(2):141-179.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
方晓思, 李佩贤, 张志军, 等.广东南雄白垩系及恐龙蛋到鸟蛋演化研究[J].地球学报, 2009, 30(2):167-186.
Google Scholar
Fang X S, Li P X, Zhang Z J, et al.Cretaceous strata in Nanxiong Basin of Guangdong and the evolution from the dinosaur egg to the bird egg[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2009, 30(2):167-186.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
曾敏德, 张金鉴.湖南洞庭盆地西部的恐龙蛋化石[J].古脊椎动物学报, 1979, 17(2):131-136.
Google Scholar
Zeng M D, Zhang J J.On the dinosaurian eggs from the western Dongting Basin, Hunan[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1979, 17(2):131-136.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
周世全, 冯祖杰, 张国建.河南恐龙蛋化石组合类型及其地层时代意义[J].现代地质, 2001, 15(4):362-369.
Google Scholar
Zhou S Q, Feng Z J, Zhang G J.Oolithias assemblages in Henan Province and its age significances[J].Geoscience, 2001, 15(4):362-369.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Chassagne-Manoukian M, Haddoumi H, Cappetta H, et al.Dating the "Red Beds" of the Eastern Moroccan High Plateaus:Evidence from late Late Cretaceous charophytes and dinosaur eggshells[J].Geobios, 2013, 46(5):371-379. doi: 10.1016/j.geobios.2013.06.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Wang X L, Wang Q, Jiang S X, et al.Dinosaur egg faunas ofthe Upper Cretaceous Terrestrial Red Beds of China and their stratigraphical significance[J].Journal of Stratigraphy, 2012, 36(2):400-416.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Grigorescu D, Garcia G, Csiki Z, et al.Uppermost Cretaceous megaloolithideggs from the Hateg Basin, Romania, associated with hadrosaur hatchlings:Search for explanation[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 293(3-4):360-374. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.03.031
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Zhao Z K, Mao X Y, Chai Z F, et al.A possible causal relationship between extinction of dinosaurs and K/T iridium enrichment in the Nanxiong Basin, South China:Evidence from dinosaur eggshells[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2002, 178:1-17. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(01)00361-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
张玉光, 裴静.河南西峡上白垩统恐龙蛋化石微量元素组成及古气候探讨[J].古生物学报, 2004, 43(2):297-302.
Google Scholar
Zhang Y G, Pei J.Trace element combinations in Upper Cretaceous dinosaur egg fossils from Xixia Basin and discussion on paleoclimate[J].Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2004, 43(2):297-302.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Bojar A V, Csiki Z, Grigorescu D.Stable isotopedistribution in Maastrichtian Vertebrates and paleosols from the Haţeg Basin, South Carpathians[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 293(3-4):329-342. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2009.08.027
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Deeming D C.Ultrastructural and functional morphology of eggshells supports the idea that dinosaur eggs were incubated buried in a substrate[J].Palaeontology, 2006, 49(1):171-185. doi: 10.1111/pala.2006.49.issue-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Tobin T S, Ward P D, Steig E J, et al.Extinction patterns, δ18O trends, and magnetostratigraphy from a southern high-latitude Cretaceous-Paleogene section:Links with Deccan volcanism[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 350-352:180-188. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.06.029
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
李艳芳, 蔡厚安, 梁汉东, 等.西峡晚白垩世恐龙蛋化石宏观矿物组成研究及意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2006, 36(2):158-163.
Google Scholar
Li Y F, Cai H A, Liang H D, et al.A study on the macro mineral compositions of the dinosaur egg fossils in the Late Cretaceous collected from Xixia Basin, Henan Province[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2006, 36(2):158-163.
Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
廖昱博, 孟耀勇, 雷浩东, 等.江西信丰恐龙蛋化石碎片的显微喇曼光谱研究[J].激光杂志, 2008, 29(6):81-82.
Google Scholar
Liao Y B, Meng Y Y, Lei H D, et al.Micro-Raman spectroscopic study of fossil dinosaur egg fragments from Jiangxi Xinfeng[J].Laser Journal, 2008, 29(6):81-82.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
赵资奎, 毛雪瑛, 柴之芳, 等.广东南雄盆地白垩系第三系(K/T)交界恐龙蛋壳的铱丰度异常[J].中国科学(D辑), 1998, 28(5):425-430.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z K, Mao X Y, Chai Z F, et al.Iridium abundance anomaly of dinosaur eggshell in the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K/T) boundary in Nanxiong Basin, Guangdong Province[J].Science in China (Series D), 1998, 28(5):425-430.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
汪晓伟, 姚肖永, 徐学义.河南西峡晚白垩世恐龙蛋化石壳微量元素组成及其对恐龙灭绝的指示意义[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5):520-527.
Google Scholar
Wang X W, Yao X Y, Xu X Y.Trace element determination of Late Cretaceous dinosaur eggshell fossils from Xixia Basin, Henan Province by ICP-OES and its implications for extinction of dinosaurs[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(5):520-527.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
王强, 黄建东, 汪筱林, 等. 皖南晚白垩世恐龙蛋化石新类型[C]//中国古生物学会: 中国古生物学会第十一次全国会员代表大会暨第27届学术年会文集, 2013: 173.
Google Scholar
Wang Q, Huang J D, Wang X L, et al.The new type of dinosaur eggs from the Upper Cretaceous of South Anhui[C]//The Palaeontological Society of China:The Proceedings of The 11th National Congress of the Palaeontological Society of China (PSC) and The 27th Annual Conference of PSC, 2013:173.
Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
余心起.皖南恐龙类化石特征及其地层划分意义[J].中国区域地质, 1998, 17(3):278-284.
Google Scholar
Yu X Q.Characteristics of dinosaur fossils from Southern Anhui and their significance for stratigraphic division[J].Regional Geology of China, 1998, 17(3):278-284.
Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
余心起, 小林快次, 吕君昌.安徽省黄山地区恐龙(足迹)脚印化石的初步研究[J].古脊椎动物学报, 1999, 37(4):285-290.
Google Scholar
Yu X Q, Kobayashi Y, Lü J C.The preliminary study of the dinosaur footprints from Huangshan, Anhui Province[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1999, 37(4):285-290.
Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
余心起, 王德恩.安徽黄山地区侏罗纪-白垩纪层序地层学特征[J].现代地质, 2001, 15(1):27-34.
Google Scholar
Yu X Q, Wang D E.Jurassic-Cretaceous sequence stratigraphy of Huangshan area in South Anhui[J].Geoscience, 2001, 15(1):27-34.
Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
朱光有, 钟建华, 周瑶琪, 等.河南西峡晚白垩世恐龙蛋化石壳超高异常Sr的发现及其意义[J].沉积学报, 1999, 17(4):659-662.
Google Scholar
Zhu G Y, Zhong J H, Zhou Y Q, et al.The dinosaur eggshell fossils of the Late Cretaceous period from Xixia Basin, Henan Province, China:Supperhigh content of strontium and its significance[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sincia, 1999, 17(4):659-662.
Google Scholar
|
| [44] |
柴之芳, 祝汉民.微量元素化学概论[M].北京:原子能出版社, 1994:1-286.
Google Scholar
Chai Z F, Zhu H M.An Introduction to Trace Element Chemistry[M].Beijing:Atomic Energy Press, 1994:1-286.
Google Scholar
|
| [45] |
卢武长, 崔秉荃, 杨绍全, 等.甘溪剖面泥盆纪海相碳酸盐岩的同位素地层曲线[J].沉积学报, 1994, 12(3):12-20.
Google Scholar
Lu W C, Cui B Q, Yang S Q, et al.Isotope stratigraphic curves of Devonian marine carbonates in Ganqi profile[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sincia, 1994, 12(3):12-20.
Google Scholar
|
| [46] |
陈友红, 朱节清, 王晓红, 等.恐龙蛋壳化石微区的元素组成与分布的质子探针研究[J].核技术, 1997, 20(3):158-163.
Google Scholar
Chen Y H, Zhu J Q, Wang X H, et al.Trace element composition and distribution in micron area of dinosaur eggshell fossils determined by proton microprobe[J].Nuclear Techniques, 1997, 20(3):158-163.
Google Scholar
|
| [47] |
张玉光, 田晓阳.再论恐龙绝灭[J].广东地质, 2003, 18(4):27-33.
Google Scholar
Zhang Y G, Tian X Y.On the extinction of dinosaur again[J].Guangdong Geology, 2003, 18(4):27-33.
Google Scholar
|
| [48] |
马配学, 柴之芳, 毛雪瑛, 等.地外撞击作用与地球灾变环境[J].地质论评, 1995, 41(1):20-27.
Google Scholar
Ma P X, Chai Z F, Mao X Y, et al.Extraterrestrial impact events and catastrophic environment of the Earth[J].Geological Review, 1995, 41(1):20-27.
Google Scholar
|
| [49] |
柴之芳, 马淑兰, 毛雪瑛, 等.浙江长兴二叠系/三叠系界线剖面的元素地球化学特征[J].地质学报, 1986(2):139-150.
Google Scholar
Chai Z F, Ma S L, Mao X Y, et al.Elemental geochemical characters at the Permian-Triassic boundary section in Changxin, Zhejiang, China[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sincia, 1986(2):139-150.
Google Scholar
|
| [50] |
Yang G C, Mao X Y, Wang J C, et al.A study on the relationshipbetween iridium concentration in hen eggshell and iridium-enriched feed by NAA[J].Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2001, 247(3):567-570. doi: 10.1023/A:1010694829831
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [51] |
周世全, 冯祖杰, 王德有.河南西峡盆地恐龙蛋化石及略论恐龙绝灭问题[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 1998, 18(5):57-63.
Google Scholar
Zhou S Q, Feng Z J, Wang D Y.The dinosaur egg fossils from the Xixia Basin, Henan with discussions on dinosaur extinction[J].Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 1998, 18(5):57-63.
Google Scholar
|
| [52] |
Russell D A.The mass extinctions of the Late Mesozoic[J].Scientific American, 1982, 246(1):58-65. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0182-58
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [53] |
Alvarez L W, Alvarez W, Asaro F, et al.Extraterrestrial cause for the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction[J].Science, 1980, 208(4448):1095-1108. doi: 10.1126/science.208.4448.1095
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [54] |
Yang W D, Chen N S, Ni S J, et al.Carbon and oxygen isotopic compositions of the carbonate rocks and the dinosaur eggshells in the Cretaceous Red Beds and their implication for paleoenvironment[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 1993, 38(23):1985-1989.
Google Scholar
|
| [55] |
赵资奎, 严正, 叶莲芳.山东莱阳恐龙蛋化石的氧、碳稳定同位素组成及其与古环境的关系[J].古脊椎动物学报, 1983, 21(3):204-209.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z K, Yan Z, Ye L F.Stable isotope composition of oxygen and carbon in the dinosaur eggshells from Laiyang, Shandong Province[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1983, 21(3):204-209.
Google Scholar
|
| [56] |
赵资奎, 叶捷, 李华梅, 等.广东省南雄盆地白垩系-第三系交界恐龙绝灭问题[J].古脊椎动物学报, 1991, 29(1):1-20.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z K, Ye J, Li H M, et al.Extinction of dinosaurs at Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary in Nanxiong Basin, Guangdong Province[J].Vertebrata PalAsiatica, 1991, 29(1):1-20.
Google Scholar
|
| [57] |
赵资奎, 严正.广东南雄盆地白垩系-第三系界线剖面恐龙蛋壳稳定同位素记录:地层及古环境意义[J].中国科学(D辑), 2000, 30(2):135-141.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z K, Yan Z.Stable isotope records of dinosaur eggs from the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary in Nanxiong Basin, Guangdong Province:Stratigraphic and paleoenvironmental significance[J].Science in China (Series D), 2000, 30(2):135-141.
Google Scholar
|
| [58] |
Grandjean P.Possible effect of lead on egg-shell thickness in Kestrels 1874-1974[J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1976, 16(1):101-106. doi: 10.1007/BF01753113
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [59] |
Pattee O H.Eggshell Thickness and reproductionin American Kestrels exposed to chronic dietary lead[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1984, 13(1):29-34. doi: 10.1007/BF01055643
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [60] |
Krampitz G P.Structure of the organic matrix in mollusc shells and avian eggshells[M]//Nancollas G H.Biological Mineralization and Demineralization.Berlin, Heidelberg, New York:Springer-Verlag, 1982:219-232.
Google Scholar
|
| [61] |
Krampitz G, Witt W.Biochemical aspects of biominera-lization[J].Topics in Current Chemistry, 1979, 78:57-144. doi: 10.1007/BFb0048190
CrossRef Google Scholar
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: