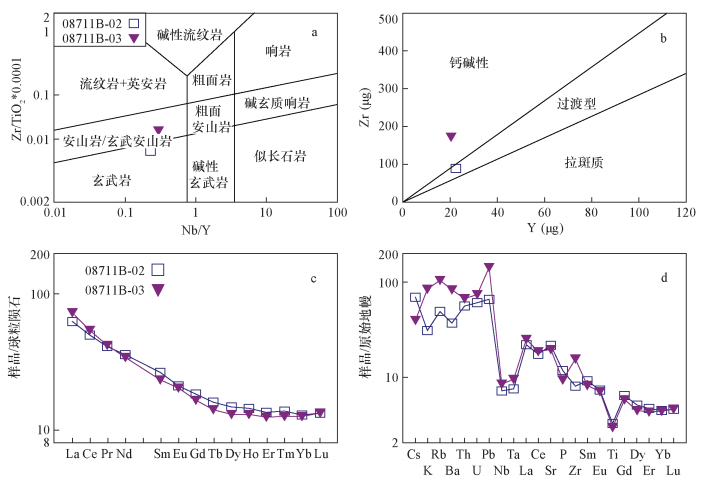
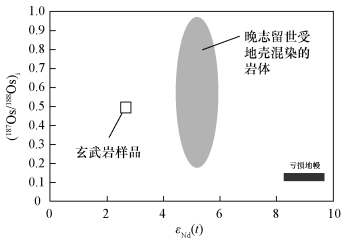
| [1] |
Chen J F, Han B F, Ji J Q, et al.Zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic implications of paleozoic plutons in northern West Junggar, north Xinjiang, China[J].Lithos, 2010, 115:137-152. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.11.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
孟磊, 申萍, 沈远超, 等.新疆谢米斯台中段火山岩岩石地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(10):3047-3056.
Google Scholar
Meng L, Shen P, Shen Y C, et al.Igneous rocks geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and its geological significance in the central section of Xiemisitai area, Xinjiang[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(10):3047-3056.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Shen P, Shen Y C, Li X H, et al.Northwestern Junggar basin, Xiemisitai mountains, China:A geochemical and geochronological approach[J].Lithos, 2012, 140-141:103-108. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Yang G X, Li Y J, Xiao W J, et al.Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the middle silurian volcanic rocks in northern West Junggar, NW China[J].International Geology Review, 2014, 56:869-884. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.905214
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Chen J F, Han B F, Zhang L, et al.Middle paleozoic initial amalgamation and crustal growth in the West Junggar (NW China):Constraints from geochronology, geochem-istry and Sr-Nd-Hf-Os isotopes of calc-alkaline and alkaline intrusions in the Xiemisitai-Saier Mountains[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113:90-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Han B F, Wang S G, Jahn B M.Depleted-mantle source for the Ulungur River A-type granites from north Xinjiang, China:Geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic evidence, and implications for phanerozoic crustal growth[J].Chemical Geology, 1997, 138:135-159. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00003-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Chen B, Jahn B M.Genesis of post-collisional granitoids and basement nature of the Junggar terrane, NW China:Nd-Sr isotope and trace element evidence[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23:691-703. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00118-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
史仁灯, 支霞臣, 陈雷, 等.Re-Os同位素体系在蛇绿岩应用研究中的进展[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(6):1685-1695.
Google Scholar
Shi R D, Zhi X C, Chen L, et al.Comments on the progress on the applications of Re-Os isotopic study on the ophiolites[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(6):1685-1695.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Chen B, Jahn B M, Suzuki K.Petrological and Nd-Sr-Os isotopic constraints on the origin of high-Mg adakitic rocks from the North China Craton:Tectonic implications[J].Geology, 2013, 41:91-94. doi: 10.1130/G33472.1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Han B F, Guo Z J, Zhang Z C, et al.Age, geochemistry, and tectonic implications of a late paleozoic stitching pluton in the north Tian Shan suture zone, Western China[J].Geological Society of American Bulletin, 2010, 122:627-640. doi: 10.1130/B26491.1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Xiao W J, Huang B C, Han C M, et al.A review of the western part of the Altaids:A key to understanding the architecture of accretionary orogens[J].Gondwana Research, 2010, 18:253-273. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.01.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Zhu Y F, Chen B, Xu X, et al.A new geological map of the western Junggar, north Xinjiang (NW China):Implications for paleoenvironmental reconstruction[J].Episodes, 2013, 36:205-220.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Yin J, Chen W, Xiao W J, et al.Late silurian-early devonian adakitic granodiorite, A-type and Ⅰ-type granites in NW Junggar, NW China:Partial melting of mafic lower crust and implications for slab roll-back[J].Gondwana Research, 2015, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.016. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.016
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
孙勇, 李永军, 杨高学, 等.西准噶尔谢米斯台山西缘中志留世火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及构造意义[J].新疆地质, 2015, 33(1):27-32.
Google Scholar
Sun Y, Li Y J, Yang G X, et al.Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and tectonic settings implication of the middle silurian volcanic rocks in the west of Xiemisitai mountain, west Junggar[J].Xinjiang Geology, 2015, 33(1):27-32.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire D C.Determination of trace elem-ents in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2000, 51:507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00318-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
贾双琳, 赵平, 杨刚, 等.混合酸敞开或高压密闭溶样-ICPMS测定地质样品中稀土元素[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(2):186-191.
Google Scholar
Jia S L, Zhao P, Yang G, et al.Quick determination of rare earth elements in geological samples with open acid digestion or high-pressure closed digestion by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(2):186-191.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
何学贤, 唐索寒, 朱祥坤, 等.多接收器等离子体质谱(MC-ICPMS)高精度测定Nd同位素方法[J].地球学报, 2007, 28(4):405-410.
Google Scholar
He X X, Tang S H, Zhu X K, et al.Precise measurement of Nd isotopic ratios by means of multi-collector magnetic sector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2007, 28(4):405-410.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
唐索寒, 李津, 梁细荣, 等.钕同位素比值143Nd/144Nd标准溶液研制[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(2):176-183.
Google Scholar
Tang S H, Li J, Liang X R, et al.Reference material preparation of 143Nd/144Nd isotope ratio[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(2):176-183.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
李超, 杨雪, 赵鸿, 等.pg-ng级Os同位素热表明电离质谱高精度分析测试技术[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(4):392-398.
Google Scholar
Li C, Yang X, Zhao H, et al.High precise isotopic measurements of pg-ng Os by negative ion thermal ionization mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(4):392-398.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Kelemen P B.Genesis of high Mg# andesites and the continental crust[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 120:1-19. doi: 10.1007/BF00311004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Tatsumi Y.Geochemical modeling of patial melting of subducting sediments and subsequent melt-mantle interaction:Generation of high-Mg andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, Southwest Japan[J].Geology, 2001, 29:323-326. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0323:GMOPMO>2.0.CO;2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Ma X H, Cao R, Zhou Z H, et al.Early cretaceous high-Mg diorites in the Yanji area, Northeastern China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97:393-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
王明梁, 唐红峰.英云闪长质熔体与地幔橄榄石反应的实验研究——对克拉通内部高镁安山岩成因的约束[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2014, 44:405-413.
Google Scholar
Wang M L, Tang H F.Reaction experiments between tonalitic melt and mantle olivine and their implications for genesis of high-Mg andesites within cratons[J].Science China:Earth Sciences, 2014, 44:405-413.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Kamei A, Owada M, Nagao T, et al.High-Mg diorites derived from Sanukitic HMA magmas, Kyushu Island, Southwest Japan Arc:Evidence from clinopyroxene and whole rock compositions[J].Lithosphere, 2004, 75:359-371.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Ma X, Chen B, Chen J F, et al.Petrogenesis and geodynamic significance of the late palaeozoic Dongwanzi complex, North China Craton:Constraints from petrological, geochemical, and Os-Nd-Sr isotopic data[J].International Geology Review, 2014, 56:1521-1540. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.948082
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Chesley J, Righter K, Ruiz J.Large scale mantle metaso-matism:A Re-Os perspective[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219:49-60. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00698-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Ren R, Han B F, Guan S W, et al.Linking the southern West Junggar terrane to the Yili block:Insights from the oldest accretionary complexes in West Junggar, NW China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences (2017), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.03.011.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Liu B, Han B F, Xu Z, et al.The cambrian initiation of intra-oceanic subduction in the southern Paleo-Asian Ocean:Further evidence from the Barleik subduction-related metamorphic complex in the West Junggar region, NW China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 123:1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.03.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
杨刚, 肖龙, 王国灿, 等.西准噶尔谢米斯台西段花岗岩年代学、地球化学、锆石Lu-Hf同位素特征及大地构造意义[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(3):548-562.
Google Scholar
Yang G, Xiao L, Wang G C, et al.Geochronology, geochemistry and zircon Lu-Hf study of granites in western section of Xiemisitai area, western Junggar[J].Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(3):548-562.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
纵瑞文, 龚一鸣, 韩非.新疆额敏东部志留纪化石的发现及其地质意义[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(3):563-572.
Google Scholar
Zong R W, Gong Y M, Han F.Discovery of silurian fossils and its geological significance in eastern Ermin, Xinjiang of NW China[J].Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2015, 40(3):563-572.
Google Scholar
|





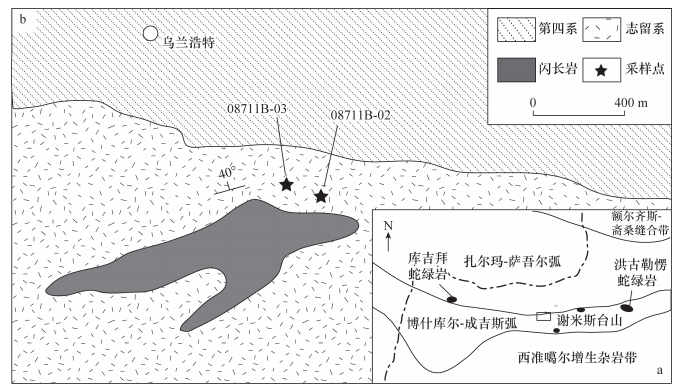

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: