| [1] |
Sharma B M, Bharat G K, Tayal S, et al.Environment and human exposure to persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in India:A systematic review of recent and historical data[J].Environment International, 2014, 66:48-64. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2014.01.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Liu J L, Wong M H.Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs):A review on environmental contamination in China[J].Environment International, 2013, 59:208-224. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2013.06.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Liu J, Zhang X.Comparative toxicity of new halophenolic DBPs in chlorinated saline wastewater effluents against a Marine Alga:Halophenolic DBPs are generally more toxic than haloaliphatic ones[J].Water Research, 2014, 65:64-72. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.024
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Harmens H, Foan L, Simon V, et al.Terrestrial mosses as biomonitors of atmospheric POPs pollution:A review[J].Environmental Pollution, 2013, 173:245-254. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.10.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Grellier J, Rushton L, Briggs D J, et al.Assessing the human health impacts of exposure to disinfection by-products-A critical review of concepts and methods[J].Environment International, 2015, 78:61-81. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.02.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Zhu Z C, Chen S J, Zheng J, et al.Occurrence of bro-minated flame retardants (BFRs), organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in agricultural soils in a BFR-manufacturing region of North China[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2014, 481:47-54. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Zhi H, Zhao Z, Zhang L.The fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in water from Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China[J].Chemosphere, 2015, 119:1134-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.09.054
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Zhao H, Wang Y, Wang R.In situ formation of well-dispersed palladium nanoparticles immobilized in imidazolium-based organic ionic polymers[J].Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(74):10871-10874. doi: 10.1039/C4CC04662E
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Tian Z, Li H, Xie H, et al.Concentration and distribution of PCNs in ambient soil of a municipal solid waste incinerator[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 491-492:75-79. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.130
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Noguera O K, Aga D S.Lessons learned from more than two decades of research on emerging contaminants in the environment[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 316:242-251. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.058
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Wu Q Y, Tang X, Huang H, et al.Antiestrogenic activity and related disinfection by-product formation induced by bromide during chlorine disinfection of sewage secondary effluent[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 273:280-286. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.03.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Sun Q, Lü M, Hu A, et al.Seasonal variation in the occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in a wastewater treatment plant in Xiamen, China[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 277:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.056
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Salihovic S, Nilsson H, Hagberg J, et al.Trends in the analysis of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in human blood[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 46:129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2012.06.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Barghi M, Shin E S, Choi S D, et al.HBCD and TBBPA in human scalp hair:Evidence of internal exposure[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 207:70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.032
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Mannetje A, Coakley J, Mueller J F, et al.Partitioning of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) between human serum and breast milk:A literature review[J].Chemosphere, 2012, 89(8):911-918. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.06.049
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Lagalante A F, Oswald T D.Analysis of Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) by liquid chromatography with negative-ion atmospheric pressure photoionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC/NI-APPI/MS/MS):Application to house dust[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2008, 391(6):2249-2256. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-2156-z
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Shin M, Svoboda M L, Falletta P.Microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) for the determination of polybrominated diphenylethers (PBDEs) in sewage sludge[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2007, 387(8):2923-2929. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1168-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Wei H, Dassanayake P S, Li A.Parametric evaluation for programmable temperaturevaporisation large volume injection in gas chromatographic determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers[J].International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 90(7):535-547. doi: 10.1080/03067310902871299
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Mackintosh S A, Pérez-Fuentetaja A, Zimmerman L R, et al.Analytical performance of a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer compared to a high resolution mass spectrometer for the analysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2012, 747:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.08.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Pizzini S, Marchiori E, Piazza R, et al.Determination by HRGC/HRMS of PBDE levels in edible mediterranean bivalves collected from North-Western Adriatic Coasts[J].Microchemical Journal, 2015, 121:184-191. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2015.03.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Parry E, Zota A R, Park J S, et al.Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and hydroxylated PBDE metabolites (OH-PBDEs):A six-year temporal trend in Northern California pregnant women[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 195:777-783. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.065
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
van den Berg M, Houba R, Leslie H A, et al.Serum levels of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in women from different European countries and possible relationships with lifestyle and diet[J].Environment International, 2017, 107:16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.06.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Chaemfa C, Xu Y, Li J, et al.Screening of atmospheric short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in India and Pakistan using polyurethane foam based passive air sampler[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(9):4799-4808.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Ma X, Zhang H, Zhou H, et al.Occurrence and gas/particle partitioning of short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in the atmosphere of Fildes Peninsula of Antarctica[J].Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 90:10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.03.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Zeng L, Wang T, Wang P, et al.Distribution and trophic transfer of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in an aquatic ecosystem receiving effluents from a sewage treatment plant[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(13):5529-5535.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Moore S, Vromet L, Rondeau B.Comparison of metasta-ble atom bombardment and electron capture negative ionization for the analysis of polychloroalkanes[J].Chemosphere, 2004, 54(4):453-459. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00709-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Wang X T, Wang X K, Zhang Y, et al.Short-and medi-um chain chlorinated paraffins in urban soils of Shanghai:Spatial distribution, homologue group patterns and ecological risk assessment[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 490:144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.121
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Zeng L, Wang T, Han W, et al.Spatial and vertical dis-tribution of short chain chlorinatedparaffins in soils from wastewater irrigated farmlands[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(6):2100-2106.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Nilsson M L, Bengtsson S, Kylin H.Identification and determination of chlorinated paraffins using multivariate evaluation of gas chromatographic data[J].Environmental Pollution, 2012, 163:142-148. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Ma X, Zhang H, Wang Z, et al.Bioaccumulation and tro-phic transfer of short chain chlorinated paraffins in a marine food web from Liaodong Bay, North China[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(10):5964-5971.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Xia D, Gao L, Zheng M, et al.A novel method for pro-filing and quantifying short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in environmental samples using GC×GC-ECNI-HRTOF-MS[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50:7601-7609.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Zencak Z, Borgen A, Reth M, et al.Evaluation of four mass spectrometric methods for the gas chromatographic analysis of polychlorinated N-alkanes[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2005, 1067(1):295-301.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Harada K H, Takasuga T, Hitomi T, et al.Dietary expo-sure to short-chain chlorinated paraffins has increased in Beijing, China[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(16):7019-7027.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Saito K, Uemura E, Ishizaki A, et al.Determination of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate by automated in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2010, 658(2):141-146. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.11.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Loos R, Tavazzi S, Paracchini B, et al.Analysis of polar organic contaminants in surface water of the Northern Adriatic Sea by solid-phase extraction followed by ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography-Qtrap® MS using a hybrid triple-quadrupole linear ion trap instrument[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2013, 405(18):5875-5885. doi: 10.1007/s00216-013-6944-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
Cao D, Hu M, Han C, et al.Proton sponge-functionalized silica as high performance adsorbents for solid-phase extraction of trace perfluoroalkyl sulfonates in the environmental water samples and their direct analysis by MALDI-TOF-MS[J].Analyst, 2012, 137(9):2218-2225. doi: 10.1039/c2an16190g
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
Li F, Zhang C, Qu Y, et al.Quantitative characterization of short-and long-chain perfluorinated acids in solid matrices in Shanghai, China[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2010, 408(3):617-623. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.032
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
Letcher R J, Chu S, McKinney M A, et al.Comparative hepatic in vitro depletion and metabolite formation of major perfluorooctane sulfonate precursors in Arctic Polar Bear, Beluga Whale, and Ringed Seal[J].Chemosphere, 2014, 112:225-231. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
Greaves A K, Letcher R J, Sonne C, et al.Brain region distribution and patterns of bioaccumulative perfluoroalkyl carboxylates and sulfonates in East Greenland Polar Bears (Ursus Maritimus)[J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2013, 32(3):713-722. doi: 10.1002/etc.2107
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
Rivière G, Sirot V, Tard A, et al.Food risk assessment for perfluoroalkyl acids and brominated flame retardants in the french population:Results from the second french total diet study[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2014, 491-492:176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.104
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
Zhang T, Qin X.Assessment of fetal exposure and mater-nal elimination of perfluoroalkyl substances[J].Environmental Science:Processes & Impacts, 2014, 16(8):1878-1881.
Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
Zhang Y, Beesoon S, Zhu L, et al.Biomonitoring of perfluoroalkyl acids in human urine and estimates of biological half-life[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(18):10619-10627.
Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
Muñoz A J, Roscales J L, Ros M, et al.Towards the implementation of the stockholm convention in Spain:Five-year monitoring (2008-2013) of POPs in air based on passive sampling[J].Environmental Pollution, 2016, 217:107-113. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.01.052
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [44] |
Gao Q, Budarin V L, Cieplik M, et al.PCDDs, PCDFs and PCNs in products of microwave-assisted pyrolysis of woody biomass-distribution among solid, liquid and gaseous phases and effects of material composition[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 145:193-199. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.110
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [45] |
Fournier A, Rychen G, Marchand P, et al.Polychlorina-ted biphenyl (PCB) decontamination kinetics in lactating goats (Capra Hircus) following a contaminated corn silage exposure[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(29):7156-7164. doi: 10.1021/jf401048j
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [46] |
Muir D, Lohmann R.Water as a new matrix for global assessment of hydrophilic POPs[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 46:162-172. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2012.12.019
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [47] |
Król S, Zabiegała B, Namies'nik J.Human hair as a biomarker of human exposure to persistent organic pollutants (POPs)[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 47:84-98. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2013.02.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [48] |
Wang X, Wang J, Jiao C, et al.Retracted:Preparation of magnetic mesoporous poly-melamine-formaldehyde composite for efficient extraction of chlorophenols[J].Talanta, 2018, 179:676-684. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.12.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [49] |
Diao C, Li C, Yang X, et al.Magnetic matrix solid phase dispersion assisted dispersive liquid liquid microextraction of ultra trace polychlorinated biphenyls in water prior to GC-ECD determination[J].Microchimica Acta, 2016, 183(3):1261-1268. doi: 10.1007/s00604-016-1761-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [50] |
Abhilash P C, Singh B, Srivastava P, et al.Remediation of lindane by Jatropha curcas L:Utilization of multipurpose species for rhizoremediation[J].Biomass and Bioenergy, 2013, 51:189-193. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.01.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [51] |
McManus S L, Coxon C E, Richards K G, et al.Quanti-tative solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography mass spectrometry analysis of the pesticides lindane, heptachlor and two heptachlor transformation products in groundwater[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1284:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.01.099
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [52] |
Marek R F, Thorne P S, Wang K, et al.PCBs and OH-PCBs in serum from children and mothers in urban and rural U.S.communities[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(7):3353-3361.
Google Scholar
|
| [53] |
Besis A, Samara C.Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the indoor and outdoor environments-A review on occurrence and human exposure[J].Environmental Pollution, 2012, 169:217-229. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.04.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [54] |
Berton P, Lana N B, Ríos J M, et al.State of the art of environmentally friendly sample preparation approaches for determination of PBDEs and metabolites in environmental and biological samples:A critical review[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 905:24-41. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.11.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [55] |
Giandomenico S, Spada L, Annicchiarico C, et al.Chlorinated compounds and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in mussels (mytilus galloprovincialis) collected from Apulia Region Coasts[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 73(1):243-251. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.05.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [56] |
van Mourik L M, Gaus C, Leonards P E G, et al.Chlori-nated paraffins in the environment:A review on their production, fate, levels and trends between 2010 and 2015[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 155:415-428. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [57] |
Geng N, Zhang H, Zhang B, et al.Effects of short-chain chlorinated paraffins exposure on the viability and metabolism of human Hepatoma Hepg2 cells[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(5):3076-3083.
Google Scholar
|
| [58] |
Gao W, Cao D, Wang Y, et al.External exposure to short-and medium-chain chlorinated paraffins for the general population in Beijing, China[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 52(1):32-39.
Google Scholar
|
| [59] |
Wang T, Wang Y, Jiang G.On the environmental health effects and socio-economic considerations of the potential listing of short-chain chlorinated paraffins into the stockholm convention on persistent organic pollutants[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(21):11924-11925.
Google Scholar
|
| [60] |
Gjoes N, Gustavsen K O.Determination of chlorinated paraffins by negative ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry[J].Analytical Chemistry, 1982, 54(8):1316-1318. doi: 10.1021/ac00245a014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [61] |
Schinkel L, Lehner S, Knobloch M, et al.Transformation of chlorinated paraffins to olefins during metal work and thermal exposure-Deconvolution of mass spectra and kinetics[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 194:803-811. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.168
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [62] |
Zafeiraki E, Costopoulou D, Vassiliadou I, et al.Deter-mination of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in various foodstuff packaging materials used in the greek market[J].Chemosphere, 2014, 94:169-176. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.092
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [63] |
Kowalczyk J, Ehlers S, Oberhausen A, et al.Absorption, distribution, and milk secretion of the perfluoroalkyl acids PFBS, PFHXS, PFOS, and PFOA by dairy cows fed naturally contaminated feed[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2013, 61(12):2903-2912. doi: 10.1021/jf304680j
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [64] |
Zhu P, Ling X, Liu W, et al.Simple and fast determi-nation of perfluorinated compounds in Taihu Lake by SPE-UHPLC-MS/MS[J].Journal of Chromatography B, 2016, 1031:61-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.07.031
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [65] |
Urtiaga A, Soriano A, Carrillo-Abad J.Bdd anodic treat-ment of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate (6:2 FTSA).Evaluation of operating variables and by-product formation[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 201:571-577. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.027
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [66] |
Xie S, Paau M C, Li C F, et al.Separation and precon-centration of persistent organic pollutants by cloud point extraction[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217(16):2306-2317. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.11.075
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [67] |
Zhu S, Gao L, Zheng M, et al.Determining indicator toxa-phene congeners in soil using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2014, 118:210-216. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.09.044
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [68] |
Xia D, Gao L, Zhu S, et al.Separation and screening of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in environmental samples using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with micro electron capture detection[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2014, 406(29):7561-7570. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-8209-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [69] |
王丹, 隋倩, 赵文涛, 等.中国地表水环境中药物和个人护理品的研究进展[J].科学通报, 2014, 59(9):743-751.
Google Scholar
|
| [70] |
Carvalho I T, Santos L.Antibiotics in the aquatic en-vironments:A review of the European Scenario[J].Environment International, 2016, 94:736-757. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.06.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [71] |
Munro K, Miller T H, Martins C P B, et al.Artificial neural network modelling of pharmaceutical residue retention times in wastewater extracts using gradient liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry data[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1396:34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.03.063
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [72] |
McEachran A D, Shea D, Bodnar W, et al.Pharma-ceutical occurrence in groundwater and surface waters in forests land-applied with municipal wastewater[J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2016, 35(4):898-905. doi: 10.1002/etc.3216
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [73] |
Kleywegt S, Pileggi V, Yang P, et al.Pharmaceuticals, hormones and bisphenol a in untreated source and finished drinking water in Ontario, Canad-Occurrence and treatment efficiency[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(8):1481-1488. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.01.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [74] |
Sui Q, Cao X, Lu S, et al.Occurrence, sources and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the groundwater:A review[J].Emerging Contaminants, 2015, 1(1):14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.emcon.2015.07.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [75] |
Fridman O, Goldberg A, Ronin I, et al.Optimization of lag time underlies antibiotic tolerance in evolved bacterial populations[J].Nature, 2014, 513(7518):418-421. doi: 10.1038/nature13469
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [76] |
Li X, Zheng W, Kelly W R.Occurrence and removal of pharmaceutical and hormone contaminants in rural wastewater treatment Lagoons[J].Science of The Total Environment, 2013, 445-446:22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.035
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [77] |
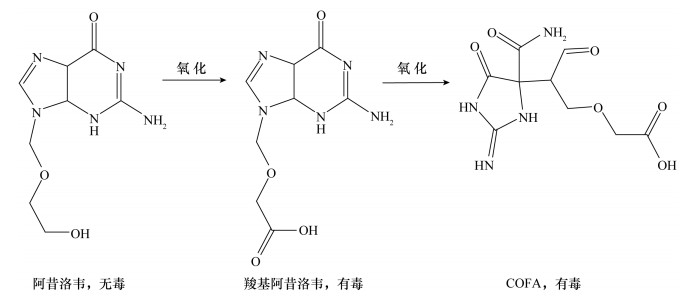
Schlüter-Vorberg L, Prasse C, Ternes T A, et al.Toxification by transformation in conventional and advanced wastewater treatment:The antiviral drug acyclovir[J].Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2015, 2(12):342-346.
Google Scholar
|
| [78] |
Prasse C, Wagner M, Schulz R, et al.Biotransformation of the antiviral drugs acyclovir and penciclovir in activated sludge treatment[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(7):2761-2769.
Google Scholar
|
| [79] |
López S R, Jurado A, Vázquez-Suñé E, et al.Occurrence of 95 pharmaceuticals and transformation products in urban groundwaters underlying the metropolis of Barcelona, Spain[J].Environmental Pollution, 2013, 174:305-315. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [80] |
Basaglia G, Pietrogrande M.Optimization of a SPME/GC/MS method for the simultaneous determination of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in waters[J].Chromatographia, 2012, 75(7-8):361-370. doi: 10.1007/s10337-012-2207-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [81] |
Vila M, Celeiro M, Lamas J P, et al., Simultaneous in-vial acetylation solid-phase microextraction followed by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of multiclass organic UV filters in water[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 323:45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.056
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [82] |
Tong L, Huang S, Wang Y, et al.Occurrence of an-tibiotics in the aquatic environment of Jianghan Plain, Central China[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 497-498:180-187. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.068
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [83] |
Radović T, Grujić S, Petković A, et al.Determination of pharmaceuticals and pesticides in river sediments and corresponding surface and ground water in the Danube River and tributaries in Serbia[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 187(1):1-17.
Google Scholar
|
| [84] |
Sumner N R, Guitart C, Fuentes G, et al.Inputs and distributions of synthetic musk fragrances in an estuarine and coastal environment:A case study[J].Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(1):215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.07.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [85] |
Rice S L, Mitra S.Microwave-assisted solvent extraction of solid matrices and subsequent detection of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2007, 589(1):125-132. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2007.02.051
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [86] |
Albero B, Sánchez B C, Miguel E, et al.Analysis of natural-occurring and synthetic sexual hormones in sludge-amended soils by matrix solid-phase dispersion and isotope dilution gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1283:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.01.113
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [87] |
Wu X, Conkle J L, Gan J.Multi-residue determination of pharmaceutical and personal care products in vegetables[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 1254:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.07.041
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [88] |
Subedi B, Mottaleb M A, Chambliss C K, et al.Simultaneous analysis of select pharmaceuticals and personal care products in fish tissue using pressurized liquid extraction combined with silica gel cleanup[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(37):6278-6284. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.07.031
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [89] |
Augusto F, Hantao L W, Mogollón N G S, et al.New materials and trends in sorbents for solid-phase extraction[J].TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 43:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2012.08.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [90] |
Spietelun A, Marcinkowski Ł, Guardia M, et al.Recent developments and future trends in solid phase microextraction techniques towards green analytical chemistry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1321:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.10.030
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [91] |
Bobeldijk I, Vissers J P C, Kearney G, et al.Screening and identification of unknown contaminants in water with liquid chromatography and quadrupole-orthogonal acceleration-time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2001, 929(1-2):63-74. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01156-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [92] |
Regli S, Chen J, Messner M, et al.Estimating potential increased bladder cancer risk due to increased bromide concentrations in sources of disinfected drinking waters[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(22):13094-13102.
Google Scholar
|
| [93] |
Richardson S D, Fasano F, Ellington J J, et al.Occu-rrence and mammalian cell toxicity of iodinated disinfection byproducts in drinking water[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(22):8330-8338.
Google Scholar
|
| [94] |
Dad A, Jeong C H, Pals J A, et al.Pyruvate remediation of cell stress and genotoxicity induced by haloacetic acid drinking water disinfection by-products[J].Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 2013, 54(8):629-637. doi: 10.1002/em.v54.8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [95] |
Stalter D, O'Malley E, Gunten U, et al.Fingerprinting the reactive toxicity pathways of 50 drinking water disinfection by-products[J].Water Research, 2016, 91:19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.047
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [96] |
Cortés C, Marcos R.Genotoxicity of Disinfection Bypro-ducts and Disinfected Waters:A Review of Recent Literature[J].Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 2018, 831:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2018.04.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [97] |
Cancho B, Ventura F, Galceran M, et al.Determination, synthesis and survey of iodinated trihalomethanes in water treatment processes[J].Water Research, 2000, 34(13):3380-3390. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00079-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [98] |
Calderón P D, Bayona J M.Development of an analytical procedure for the determination of trihalomethanes in leafy vegetable by headspace-spme followed by GC-ECD determination[J].Food Analytical Methods, 2015, 8(5):1093-1100. doi: 10.1007/s12161-014-9965-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [99] |
Kubáň P, Makarõtševa N, Kiplagat I K, et al.Deter-mination of five priority haloacetic acids by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection and solid phase extraction preconcentration[J].Journal of Separation Science, 2012, 35(5-6):666-673. Wang D, Sui Q, Zhao W T, et al.Pharmaceutical and personal care products in the surface water of China:A review[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(9):743-751. doi: 10.1002/jssc.v35.5/6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [100] |
Teh H B, Li S F Y.Simultaneous determination of bromate, chlorite and haloacetic acids by two-dimensional matrix elimination ion chromatography with coupled conventional and capillary columns[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1383:112-120. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.01.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [101] |
Nsubuga H, Basheer C.Determination of haloacetic acids in swimming pool waters by membrane-protected micro-solid phase extraction[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1315:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.09.050
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [102] |
Alhooshani K, Basheer C, Kaur J, et al.Electromem-brane extraction and HPLC analysis of haloacetic acids and aromatic acetic acids in wastewater[J].Talanta, 2011, 86:109-113. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2011.08.026
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [103] |
Prieto-Blanco M C, Alpendurada M F, López-Mahía P, et al.Improving methodological aspects of the analysis of five regulated haloacetic acids in water samples by solid-phase extraction, ion-pair liquid chromatography and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2012, 94:90-98. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2012.02.061
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [104] |
Kubwabo C, Stewart B, Gauthier S A, et al.Improved derivatization technique for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry determination of 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2(5h)-furanone in drinking water[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2009, 649(2):222-229. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2009.07.035
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [105] |
Planas C, Ventura F, Caixach J, et al.Analysis of 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethyl)-5-hydroxy-2(5h) -furanone (MX) and its brominated analogues in chlorine-treated water by gas chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (GC-QQQ-MS/MS)[J].Talanta, 2015, 144:145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.033
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [106] |
Luo Q, Chen X, Wei Z, et al.Simultaneous and high-throughput analysis of iodo-trihalomethanes, haloacetonitriles, and halonitromethanes in drinking water using solid-phase microextraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry:An optimization of sample preparation[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2014, 1365:45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.09.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [107] |
Gilchrist E S, Healy D A, Morris V N, et al.A review of oxyhalide disinfection by-products determina-tion in water by ion chromatography and ion chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 942:12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.09.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [108] |
Subedi B, Usenko S.Enhanced pressurized liquid extraction technique capable of analyzing polychlorodibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorodibenzofurans, and polychlorobiphenyls in fish tissue[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 1238:30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.03.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: