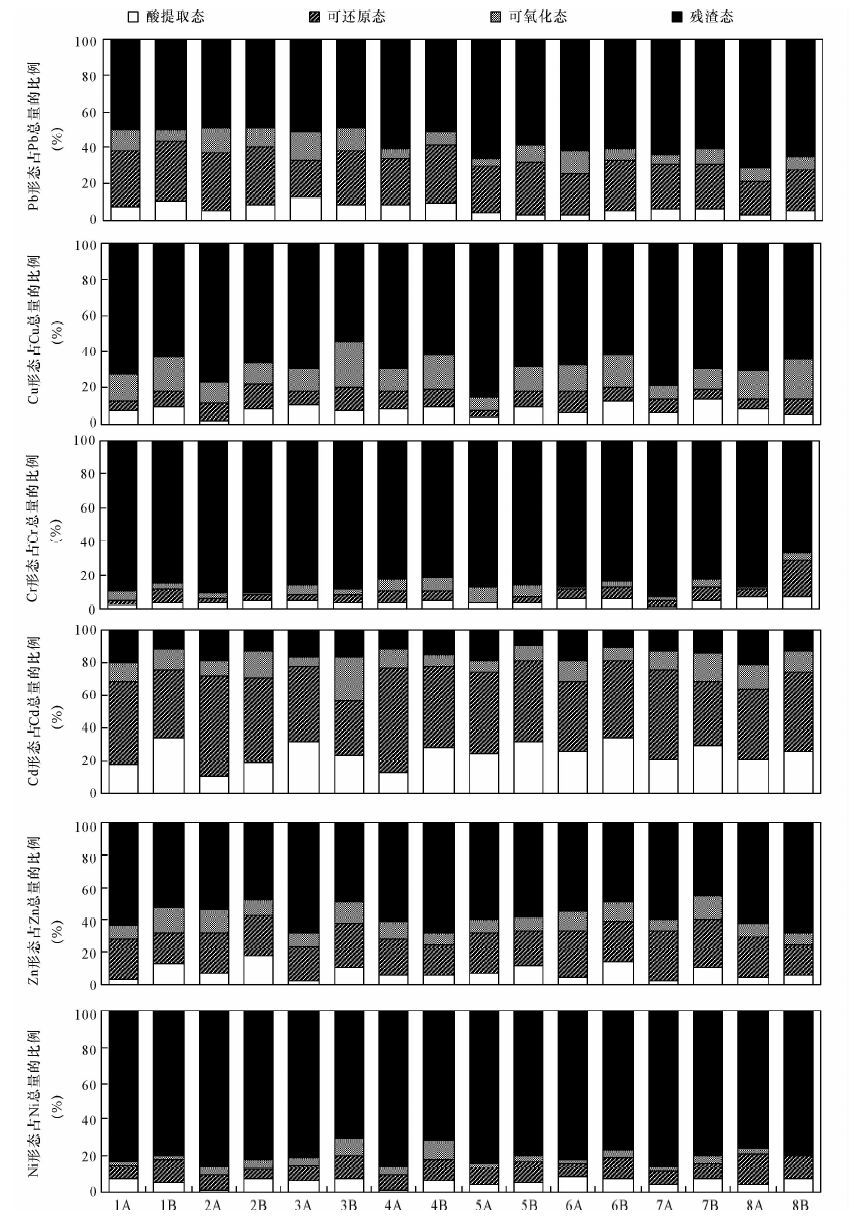
| [1] |
Soodana R K,Pakadeb Y B,Nagpala A,et al.Analytical Techniques for Estimation of Heavy Metals in Soil Ecosystem:A Tabulated Review[J].Talanta,2014,125:405-410. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.02.033
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Shao X X,Huang B,Zhao Y C,et al.Impacts of Human Activities and Sampling Strategies on Soil Heavy Metal Distribution in a Rapidly Developing Region of China[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2014,104:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.02.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Yao Z,Li J H,Xie H H,et al.Review on Remediation Technologies of Soil Contaminated by Heavy Metals[J].Procedia Environmental Sciences,2012,16:722-729. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.099
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Bao Y H,Gao P,He X B.The Water-Level Fluctuation Zone of Three Gorges Reservoir-A Unique Geomor-phological Unit[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2015,150:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.07.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
王图锦,胡学斌,吉芳英,等.三峡库区淹没区土壤重金属形态分布及其对水质影响[J].环境科学研究,2010,23(2):158-164.
Google Scholar
Wang T J,Hu X B,Ji F Y,et al.Chemical Fraction Composition Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Submerged Soil of Three Gorges Reservoir Area and Effect on Water Quality[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2010,23(2):158-164.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
曹琳,吉芳英.三峡库区消落带干湿交替表层沉积物磷分布特征[J].地球与环境,2013,41(2):126-131.
Google Scholar
Cao L,Ji F Y.Phosphorus Distribution Characteristics in Dry-Wet Alteration Sediment of Fluctuation Zone in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J].Earth and Environ-ment, 2013,41(2):126-131.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
朱宏伟,贺秀斌,胡云华,等.三峡库区消落带土壤磁性变化规律及成因探讨[J].现代地质,2014,28(4):859-866.
Google Scholar
Zhu H W,He X B,Hu Y H,et al.Discussion of Characteristics and Origin of Soil Magnetism Changes in the Three-Gorge Reservoir Riparian Zone[J].Geoscience,2014,28(4):859-866.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Chen Y,Li S Y,Zhang Y L,et al.Assessing Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Water-Level-Fluctuation Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir,China[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,191:366-372. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.090
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
胥焘,王飞,郭强,等.三峡库区香溪河消落带及库岸土壤重金属迁移特征及来源分析[J].环境科学,2014,305(4):1502-1508.
Google Scholar
Xu T,Wang F,Guo Q,et al.Transfer Characteristic and Source Identification of Soil Heavy Metals from Water-Level-Fluctuating Zone along Xiangxi River,Three-Gorges Reservoir Area[J].Environmental Science,2014,305(4):1502-1508.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
张成,陈宏,孙荣国,等.三峡水库消落带不同水位高程土壤汞风险评价[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(1):242-252.
Google Scholar
Zhang C,Chen H,Sun R G,et al.Risk Assessment of Mercury in Soil at Different Water-Level Altitudes in Drawdown Areas of Three Gorges Reservior[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,28(1):242-252.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
余杨,王雨春,周怀东,等.三峡库区蓄水初期大宁河重金属食物链放大特征研究[J].环境科学,2013,34(10):3847-3853.
Google Scholar
Yu Y,Wang Y C,Zhou H D,et al.Biomagnification of Heavy Metals in the Aquatic Food Chain in Daning River of the Three Gorges Reservoir during Initial Impoundment[J].Environmental Science,2013,34(10):3847-3853.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
张晨光,徐德星,张乃明,等.大宁河回水区消落带土壤磷释放动力学研究[J].土壤通报,2011,42(5):1159-1164.
Google Scholar
Zhang C G,Xu D X,Zhang N M,et al.Phosphorus Release Kinetics of the Soils from the Backwater-Fluctuating Zones of Daning River[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2011,42(5):1159-1164.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
许超,夏北成,吴海宁,等.酸性矿山废水污灌区水稻土重金属的形态分布及生物有效性[J].环境科学,2009,30(3):900-906.
Google Scholar
Xu C,Xia B C,Wu H N,et al.Speciation and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Paddy Soil Irrigated by Acid Mine Drainage[J].Environmental Science,2009,30(3):900-906.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Forstner U.Sediments and Environmental Geochemistry:Selected Aspects and Case Histories[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag,1990:311-338.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
唐将,钟远平,王力.三峡库区土壤重金属背景值研究[J].中国生态农业学报,2008,16( 4) :848-852. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2008.00848
CrossRef Google Scholar
Tang J,Zhong Y P,Wang L.Background Value of Soil Heavy Metal in the Three Gorges Reservoir District[J].Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2008,16(4):848-852. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2008.00848
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Saleem M,Iqbal J,Shah M H.Geochemical Speciation,Anthropogenic Contamination,Risk Assessment and Source Identification of Selected Metals in Freshwater Sediments-A Case Study from Mangla Lake,Pakistan[J].Environmental Nanotechnology,Monitoring & Management,2015,4:27-36.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Chen H Y,Teng Y G,Lu S J,et al.Contamination Features and Health Risk of Soil Heavy Metals in China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2015,512-513:143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Zhao S,Feng C H,Wang D X,et al.Salinity Increases the Mobility of Cd,Cu,Mn,and Pb in the Sediments of Yangtze Estuary:Relative Role of Sediments' Properties and Metal Speciation[J].Chemosphere,2013,91:977-984. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Yang Z F,Wang Y,Shen Z Y,et a1.Distribution and Speciation of Heavy Metals in Sediments from the Mainstream,Tributaries,and Lakes of the Yangtze River Catchment of Wuhan,China[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,166:1186-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.034
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Wei X,Han L F,Gao B,et a1.Distribution,Bioavai-lability,and Potential Risk Assessment of the Metals in Tributary Sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir:The Impact of Water Impoundment[J].Ecological Indicators,2016,61:667-675. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.10.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
钟晓兰,周生路,黄明丽,等.土壤重金属的形态分布特征及其影响因素[J].生态环境学报,2009,18 (4):1266-1273.
Google Scholar
Zhong X L,Zhou S L,Huang M L,et al.Chemical Form Distribution Characteristics of Soil Heavy Metals and Its Influencing Factors[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2009,18(4):1266-1273.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
陈媛,郭秀锐,程水源,等.基于SWAT模型的三峡库区流域污染物来源分析及重点控制区域识别[J].北京工业大学学报,2013,39(5):761-768.
Google Scholar
Chen Y,Guo X R,Cheng S Y,et al.Pollutant Source Analysis and Identification of Prior Control Areas in Three Gorges Reservoir Based on SWAT Model[J].Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2013,39(5):761-768.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
高银超,鲍玉海,唐强,等.基于AnnAGNPS模型的三峡库区小江流域非点源污染负荷评价[J].长江流域资源与环境,2012,21(1):119-126.
Google Scholar
Gao Y C,Bao Y H,Tang Q,et al.Applying AnnAGNPS to Estimate Non-point Pollution Loading from Xiao Jiang Basin in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region[J].Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2012,21(1):119-126.
Google Scholar
|





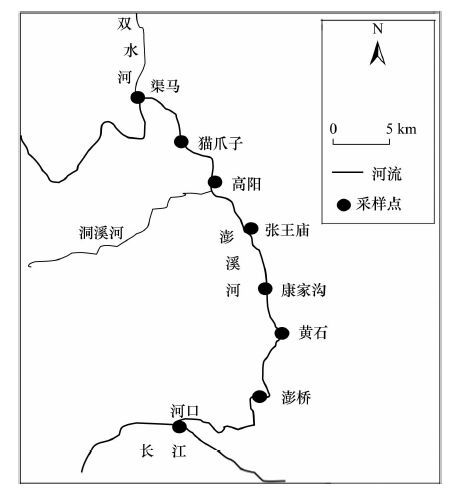

 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
