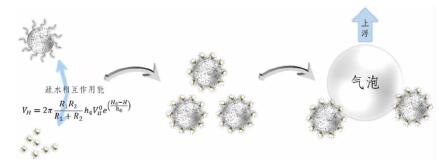
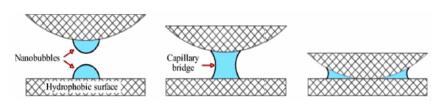
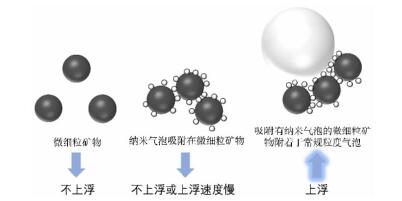
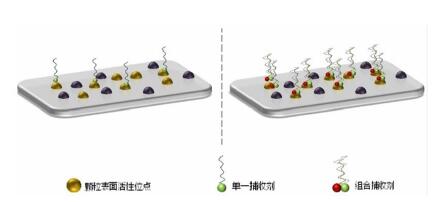
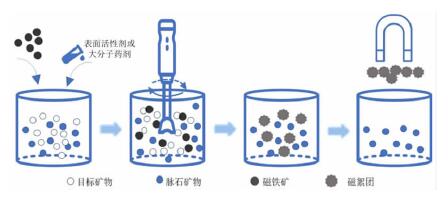
| [1] |
李纲, 杨斌, 刘清华, 等.南岭成矿带西段苗儿山岩体外围钨矿成矿作用综合研究思路[J].国土资源导刊, 2014, 11(10):55-62.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
张曙光, 李晓阳, 张杰.兰坪难选氧化铅锌矿浮选工艺研究[J].云南冶金, 2005, 34(5):11-13.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
陈骏, HALLS C., STANLEY C. J.湖南柿竹园钨-钼-铋-锡矿床中锡石的产状与成因[J].地质论评, 1992, 38(2):164-172.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
WEI Z, HU Y, HAN H, et al. Selective separation of scheelite from calcite by self-Assembly of H2SiO3 polymer using Al3+ in Pb-BHA flotation[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(1):43.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
姚伟, 李茂林, 崔瑞, 等.微细粒矿物的分选技术[J].现代矿业, 2015(1):66-69, 152.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
李淑菲, 李强.微细粒白钨矿浮选研究现状[J].有色冶金节能, 2019, 35(3):12-15.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
DERVAGIN B V, DUKHIN S S, RULEV N N. Kinetic theory of the flotation of small particles[J]. Russian Chemical Reviews, 1984, 51(1):51-67.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
FORBES E. Shear, selective and temperature responsive flocculation:A comparison of fine particle flotation techniques[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2011, 99(1-4):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2011.02.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
YIN W, YANG X, ZHOU D, et al. Shear hydrophobic flocculation and flotation of ultrafine Anshan hematite using sodium oleate[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(3):652-664. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60762-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
秦煦坤, 钱玉鹏, 高惠民, 等.剪切絮凝强化浮选微细粒红柱石试验[J].金属矿山, 2017(9):115-119.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
徐凤平, 冯其明, 张国范, 等.湖南某白钨矿浮选试验研究[J].矿冶工程, 2016, 36(2):38-40.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
HUANG X, XIAO W, ZHAO H, et al. Hydrophobic flocculation flotation of rutile fines in presence of styryl phosphonic acid[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(7):1424-1432. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64781-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
FORBES E. Shear, selective and temperature responsive flocculation:A comparison of fine particle flotation techniques[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2011, 99(1):1-10.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
FARROKHPAY S, MORRIS G E, FORNASIERO D, et al. Stabilisation of titania pigment particles with anionic polymeric dispersants[J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 202(1):143-150.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
FARROKHPAY S. The importance of rheology in mineral flotation:A review[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2012, 36-38:272-278. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2012.05.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
LUCKHAM P F, ROSSI S. The colloidal and rheological properties of bentonite suspensions[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 1999, 82(1):43-92.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
SHI F N, NAPIER-MUNN T J. A model for slurry rheology[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1997, 23(7):64.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
CHEN W, CHEN F, BU X, et al. A significant improvement of fine scheelite flotation through rheological control of flotation pulp by using garnet[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 138:257-266. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.05.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
LASKOWSKI J, NDLOVU B, KILICKAPLAN I. Rheology of aqueous suspensions of needle-like mineral particles[J]. Proc 8th UBC-McGill-UA International Symposium on the Fundamentals of Mineral Processing:Rheology and Processing of Fine Particles, 2010:193-203.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
NG W S, SONSIE R, FORBES E, et al. Flocculation/flotation of hematite fines with anionic temperature-responsive polymer acting as a selective flocculant and collector[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 77:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2015.02.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
HAO H, LI L, SOMASUNDARAN P, et al. Adsorption of pregelatinized starch for selective flocculation and flotation of fine siderite[J]. Langmuir, 2019, 35(21):6878-6887. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00669
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
杨招君, 徐晓衣, 袁祥奕.低品位锡细泥选择性絮凝浮选试验研究[J].中国矿业, 2019, 28(S1):212-215.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
潘庆庆, 彭会清.用新型絮凝剂PG改善某钨细泥的浮选效果[J].金属矿山, 2018(5):98-102.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
李树磊.微细粒辉钼矿选择性絮凝-浮选基础研究[D].徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
ZOU W, GONG L, HUANG J, et al. Adsorption of hydrophobically modified polyacrylamide P(AM-NaAA-C16DMAAC) on model coal and clay surfaces and the effect on selective flocculation of fine coal[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 142:105887. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.105887
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
LI L, HAO H, YUAN Z, et al. Regulating effects of citric acid and pregelatinized starch on selective flocculation flotation of micro-fine siderite[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2020, 315:113726. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113726
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
GREENE E W, DUKE J B. Selective froth flotation of ultrafine minerals or slimes[J]. Trans. AIME, 1962, 223:389-395.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
S·科卡, 周廷熙.从高岭土中载体浮选明矾石[J].国外金属矿选矿, 2001(9):42-45.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
陈秀珍.疏水性聚合物对细粒级白钨矿载体浮选的工艺和机理研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2014.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
冷文华, 朱龙华, 冯其明.钨矿物浮选研究进展[J].矿产保护与利用, 1999(5):3-5.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
ZHOU S, WANG X, BU X, et al. A novel flotation technique combining carrier flotation and cavitation bubbles to enhance separation efficiency of ultra-fine particles[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2020, 64(105005):105005.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
ZHANG X, HU Y, SUN W, et al. The effect of polystyrene on the carrier flotation of fine smithsonite[J]. Minerals, 2017, 7(524).
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
肖骏, 陈代雄.聚苯乙烯载体浮选微细粒白钨矿研究[J].中国钨业, 2015, 30(6):14-20.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
梁瑞禄, 沼田芳明, 藤田丰久, 等.关于微细粒锡矿石载体浮选的研究——不同载体种类的影响[J].国外金属矿选矿, 1999(8):7-12.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
邱冠周, 胡岳华, 王淀佐.微细粒赤铁矿载体浮选机理研究[J].有色金属, 1994(4):23-28.
Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
朱阳戈.微细粒钛铁矿浮选理论与技术研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
王纪镇.复杂难处理白钨矿浮选分离的强化及其机理研究[D].沈阳: 东北大学, 2015.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
王纪镇, 印万忠, 孙忠梅.碳酸钠对白钨矿自载体浮选的影响及机理[J].工程科学学报, 2019, 41(2):174-180.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
胡为柏, 王淀佐, 邱冠周.分支载体浮选的理论与实践[J].中南矿冶学院学报, 1987(4):408-414.
Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
李天霞, 张晓峰, 张适合, 等.河北某铜尾矿综合回收铜的选矿试验研究[J].有色金属(选矿部分), 2019(2):17-22.
Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
秦永红, 杨光, 马自飞, 等.某微细粒级混磁精矿载体浮选试验研究[J].金属矿山, 2019(2):76-80.
Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
XING Y, GUI X, PAN L, et al. Recent experimental advances for understanding bubble-particle attachment in flotation[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 246:105-132. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.05.019
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
何桂春, 王玉彤, 康倩.纳米技术在微细粒矿物浮选中的应用[J].有色金属科学与工程, 2015, 6(2):57-62.
Google Scholar
|
| [44] |
FAN M, TAO D, HONAKER R, et al. Nanobubble generation and its application in froth flotation (part I):nanobubble generation and its effects on properties of microbubble and millimeter scale bubble solutions[J]. Mining Science and Technology (China), 2010, 20(1):1-19. doi: 10.1016/S1674-5264(09)60154-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [45] |
岳双凌, 廖寅飞, 马子龙.选择性絮凝-柱浮选回收钼精选尾矿中的微细粒辉钼矿[J].矿产综合利用, 2018(5):52-57.
Google Scholar
|
| [46] |
刘炯天, 李小兵, 王永田, 等.旋流-静态微泡浮选柱浮选某难选钼矿的试验研究[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2008(2):300-306.
Google Scholar
|
| [47] |
FARROKHPAY S, FILIPPOVA I, FILIPPOVA L, et al. Flotation of fine particles in the presence of combined microbubbles and conventional bubbles[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 155:106439. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106439
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [48] |
CALGAROTO S, AZEVEDO A, RUBIO J. Flotation of quartz particles assisted by nanobubbles[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2015, 137:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2015.02.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [49] |
R A F, RUBIO J. On the role of nanobubbles in particle-bubble adhesion for the flotation of quartz and apatitic minerals[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 127:178-184. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2018.08.020
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [50] |
廖世双, 欧乐明, 周伟光.空化过程微纳米气泡性质及其对细粒矿物浮选的影响[J].中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(7):1567-1574.
Google Scholar
|
| [51] |
陈冲.某风化白钨细泥高效回收试验研究[D].徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2015.
Google Scholar
|
| [52] |
黄光耀, 冯其明, 欧乐明, 等.利用微泡浮选柱从浮选尾矿中回收微细粒级白钨矿[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(2):263-267.
Google Scholar
|
| [53] |
YOON R H, LUTTREL G H. The effect of bubble size on fine particle flotation[J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review, 1989, 5(1-4):101-122. doi: 10.1080/08827508908952646
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [54] |
XING Y, XU M, GUO F, et al. Role of different types of clay in the floatability of coal:Induction time and bubble-particle attachment kinetics analysis[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 344:814-818. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.12.074
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [55] |
FAN M, TAO D, HONAKER R, et al. Nanobubble generation and its applications in froth flotation (part Ⅲ):specially designed laboratory scale column flotation of phosphate[J]. Mining Science and Technology (China), 2010, 20(3):317-338. doi: 10.1016/S1674-5264(09)60205-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [56] |
XIAO W, ZHAO Y, YANG J, et al. Effect of sodium oleate on the adsorption morphology and mechanism of nanobubbles on the mica Surface[J]. Langmuir, 2019, 35(28):9239-9245. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b01384
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [57] |
冯其明, 周伟光, 石晴.纳米气泡的形成及其对微细粒矿物浮选的影响[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 48(1):9-15.
Google Scholar
|
| [58] |
AHMADI R, KHODADADI D A, ABDOLLAHY M, et al. Nano-microbubble flotation of fine and ultrafine chalcopyrite particles[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2014, 24(4):559-566. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.05.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [59] |
HAMPTON M A, NGUYEN A V. Nanobubbles and the nanobubble bridging capillary force[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 154(1-2):30-55. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2010.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [60] |
AHMADI R, KHODADADI D A, ABDOLLAHY M, et al. Nano-microbubble flotation of fine and ultrafine chalcopyrite particles[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2014, 24(4):559-566. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2014.05.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [61] |
ZHOU W, CHEN H, OU L, et al. Aggregation of ultra-fine scheelite particles induced by hydrodynamic cavitation[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2016, 157:236-240. doi: 10.1016/j.minpro.2016.11.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [62] |
程建国.应用基团电负性理论计算和同分异构原理发展新型锡石捕收剂[J].矿冶工程, 1986(4):18-21.
Google Scholar
|
| [63] |
王淀佐, 林强, 蒋玉仁.选矿与冶金药剂分子设计[M].长沙:中南工业大学出版社, 1996.
Google Scholar
|
| [64] |
王帅, 王明月, 杨佳, 等.有机磷选冶药剂的合成与应用[J].矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(2):1-9.
Google Scholar
|
| [65] |
WANG S. S., AVOFINS P. V., 王淀佐.二烷基二硫代次膦酸在硫化矿浮选中的应用[J].国外金属矿选矿, 1984(9):41-47.
Google Scholar
|
| [66] |
杨晓玲, 王淀佐.二烷基硫化磷酸铵的捕收性能[J].山东冶金, 1997, 019(4):32-34, 49.
Google Scholar
|
| [67] |
林强, 杨晓玲, 王淀佐.一类螯合捕收剂α-肟基膦酸酯的制备及其结构与性能的关系[J].过程工程学报, 1997(4):312-317.
Google Scholar
|
| [68] |
HAN H, XIAO Y, HU Y, et al. Replacing Petrov's process with atmospheric flotation using Pb-BHA complexes for separating scheelite from fluorite[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 145:106053. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.106053
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [69] |
孙宁, 高建德, 于凯, 等.镁离子对钼尾矿中石英和长石浮选分离的影响研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(2):30-35.
Google Scholar
|
| [70] |
孙青, 王帅, 钟宏.肟类选冶药剂的合成与应用[J].矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(2):10-16.
Google Scholar
|
| [71] |
梁欢, 代典, 何东升, 等.α-磺酸基棕榈酸捕收剂的合成及其对白云石和氟磷灰石的分选性能研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(2):23-29.
Google Scholar
|
| [72] |
艾光华, 吴燕玲, 周源, 等.组合捕收剂从含钙矿物浮选体系中回收微细粒白钨矿[J].有色金属工程, 2014, 4(6):44-47.
Google Scholar
|
| [73] |
罗思岗, 赵志强, 刘建远, 等.新型捕收剂BKG721在贵金属矿浮选中的应用研究[J].有色金属(选矿部分), 2018(4):85-88.
Google Scholar
|
| [74] |
HE T, LI H, JIN J, et al. Improving fine molybdenite flotation using a combination of aliphatic hydrocarbon oil and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon[J]. Results in Physics, 2019, 12:1050-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2018.12.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [75] |
胡文英.组合捕收剂浮选微细粒黑钨矿作用机理与应用研究[D].赣州: 江西理工大学, 2013.
Google Scholar
|
| [76] |
徐龙华, 田佳, 巫侯琴, 等.组合捕收剂在矿物表面的协同效应及其浮选应用综述[J].矿产保护与利用, 2017(2):107-112.
Google Scholar
|
| [77] |
LUO L, NGUYEN A V. A review of principles and applications of magnetic flocculation to separate ultrafine magnetic particles[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 172:85-99. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2016.07.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [78] |
唐雪峰, 陈雯, 余永富, 等.细粒铁矿选矿中选择性絮凝的研究与应用[J].金属矿山, 2010(9):44-46.
Google Scholar
|
| [79] |
周艳飞.疏水团聚-磁种法从赤泥中回收铁及机理研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2009.
Google Scholar
|
| [80] |
张汉泉, 周峰, 殷佳琪, 等.选择性絮凝-磁种法在微细粒人工磁铁矿磁选中的团聚效应[J].矿冶, 2019, 28(4):42-50.
Google Scholar
|
| [81] |
LU J, YUAN Z, WANG N, et al. Selective surface magnetization of pentlandite with magnetite and magnetic separation[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 317:162-170. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.04.031
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [82] |
GOGOI M, BORUAH P, SENGUPTA P, et al. Separation of ultrafine chalcogenide particles using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and ligands with metal selectivity[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 137:147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.04.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [83] |
欧阳超, 卢毅屏, 冯其明, 等.油酸钠作用下磁铁矿与硫化矿物间异相聚团研究[J].矿冶工程, 2018, 38(2):34-37.
Google Scholar
|
| [84] |
胡岳华, 邱冠周, 王淀佐.细粒浮选体系中扩展的DLVO理论及应用[J].中南矿冶学院学报, 1994(3):310-314.
Google Scholar
|
| [85] |
GRAY S R, LANGBERG D E, GRAY N B. Fine mineral recovery with hydrophobic magnetite[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1994, 41(3-4):183-200. doi: 10.1016/0301-7516(94)90027-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [86] |
ANASTASSAKIS G N. Separation of fine mineral particles by selective magnetic coating[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Ence, 2002, 256(1):114-120.
Google Scholar
|





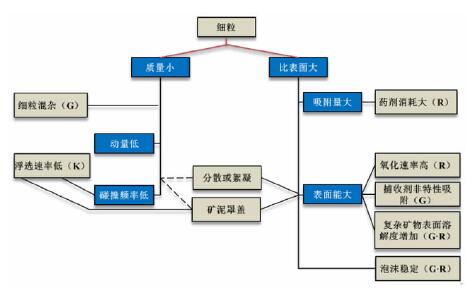

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: