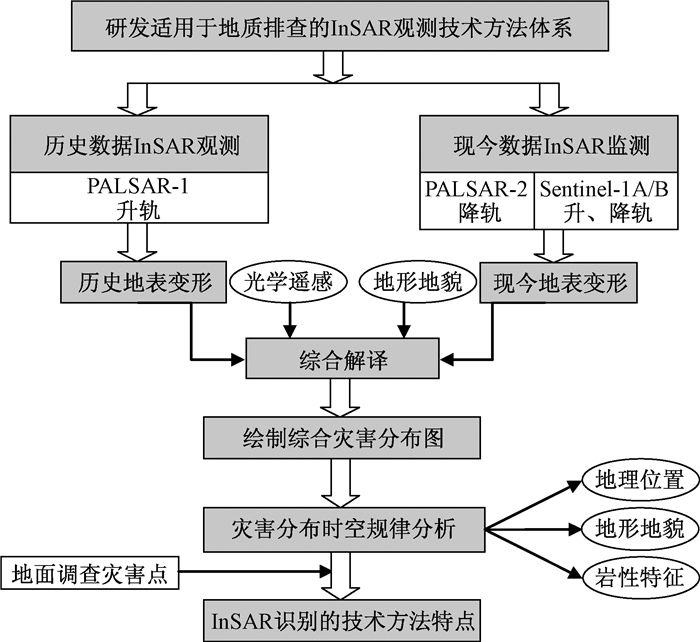
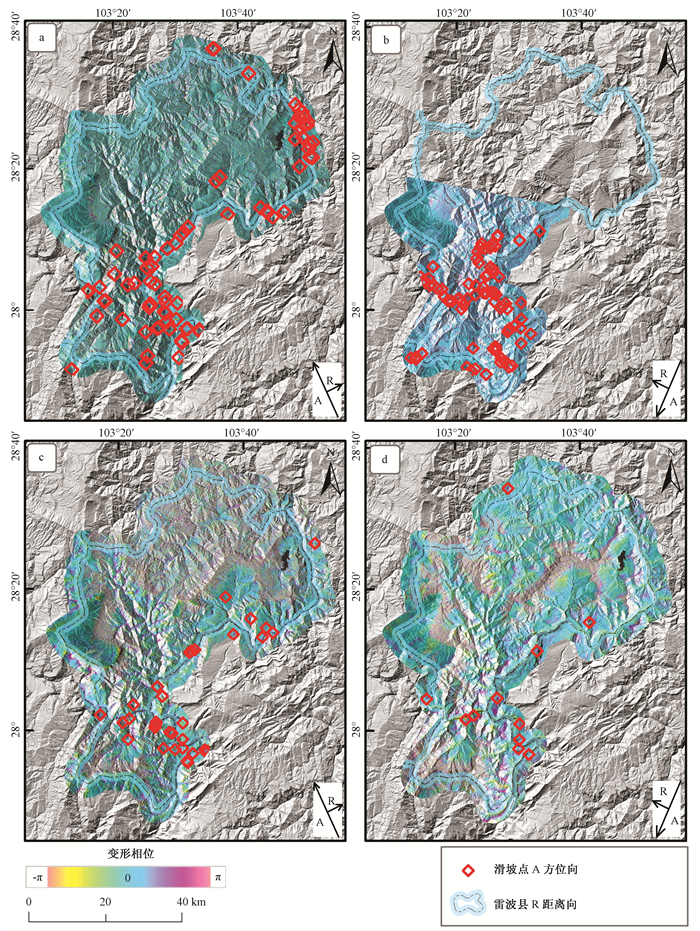
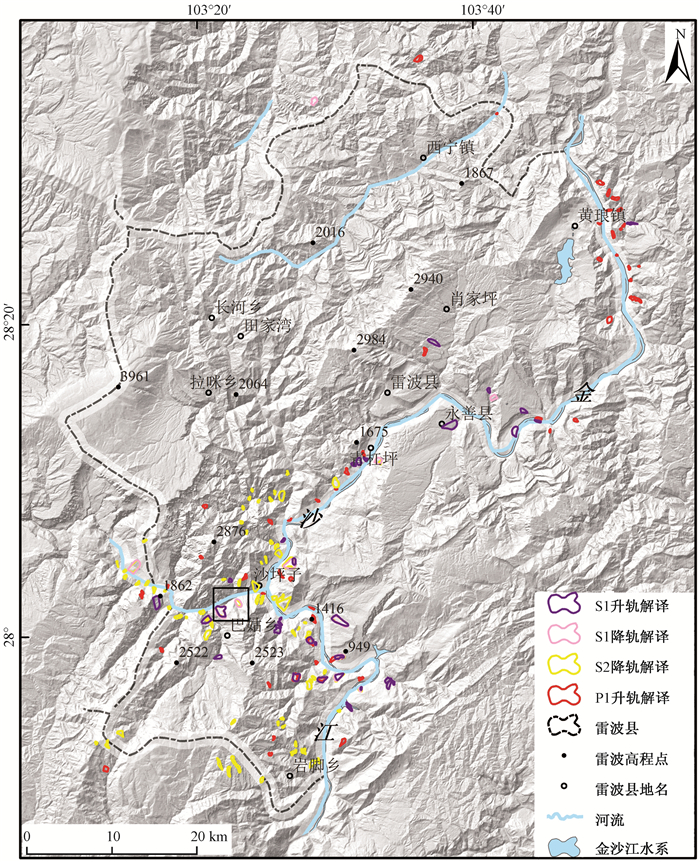
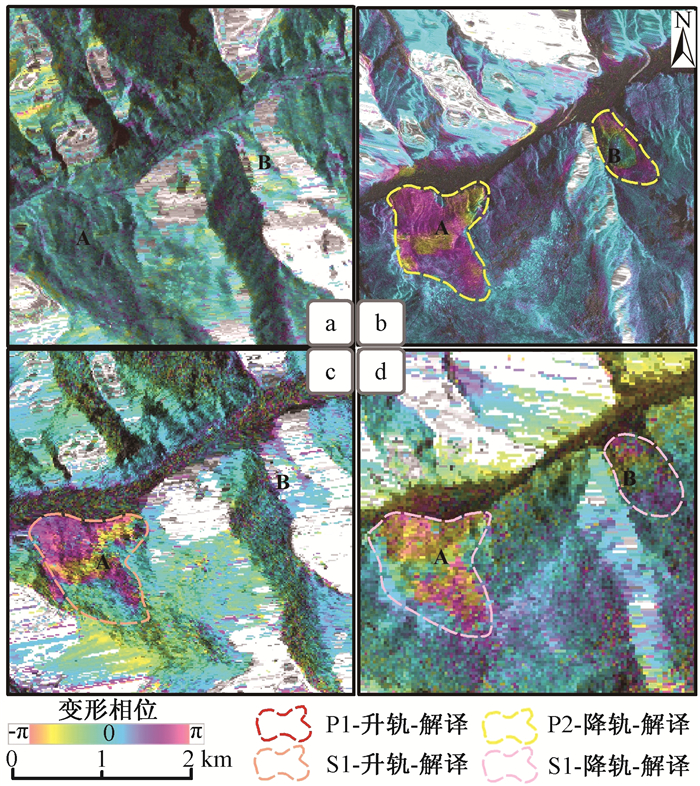
|
许强, 汤明高, 徐开祥, 等.滑坡时空演化规律及预警预报研究[J].岩石力学与工程学, 2008, 27(6):1104~1112.
Google Scholar
XU Qiang, TANG Minggao, XU Kaixiang, et al. Research on space-time evolution laws and early warning-prediction of landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(6):1104~1112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Google Scholar
|
|
Ferretti A. Satellite InSAR data:reservoir monitoring from space[M]. Houten:European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, 2014.
Google Scholar
|
|
廖明生, 王腾.时间序列InSAR技术与应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014.
Google Scholar
LIAO Mingsheng, WANG Teng. Time series InSAR technology and application[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
Google Scholar
|
|
Fruneau B, Achache J, Delacourt C. Observation and modelling of the Saint-Étienne-de-Tinée landslide using SAR interferometry[J]. Tectonophysics, 1996, 265(3/4):181~190.
Google Scholar
|
|
Rott H, Scheuchl B, Siegel A, et al. Monitoring very slow slope movements by means of SAR interferometry:a case study from a mass waste above a reservoir in the Ötztal Alps, Austria[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1999, 26(11):1629~1632. doi: 10.1029/1999GL900262
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
Yin, Y., Zheng, W., Liu, Y., et al. Integration of GPS with InSAR to monitoring of the Jiaju landslide in Sichuan, China[J]. Landslides, 2010, 7:359~365. doi: 10.1007/s10346-010-0225-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
Yao X, Li L J, Zhang Y S, et al. Types and characteristics of slow-moving slope geo-hazards recognized by TS-InSAR along Xianshuihe active fault in the eastern Tibet Plateau[J]. Natural Hazards, 2017, 88(3):1727~1740. doi: 10.1007/s11069-017-2943-y
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
|
陈进, 徐平.金沙江科学考察的几个问题及思考[J].长江科学院院报, 2013, 30(7):1~6.
Google Scholar
CHEN Jin, XU Ping. Considerations on the scientific investigation of Jinsha River[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2013, 30(7):1~6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Google Scholar
|
|
曾陈萍, 张宏平.物联网技术在山洪灾害监测预警系统中的应用研究[J].西昌学院学报·自然科学版, 2014, 28(3):56~59.
Google Scholar
ZENG Chenping, ZHANG Hongping. A review of the application of internet of things in the mountain torrent disaster monitoring and early-warning system[J]. Journal of Xichang College·Natural Science Edition, 2014, 28(3):56~59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Google Scholar
|
|
孙瑜, 李宏俊, 曹树波, 等.四川雷波碉楼沟泥石流特征及防治对策[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 2017, 28(1):1~6.
Google Scholar
SUN Yu, LI Hongjun, CAO Shubo, et al. Features and preventive countermeasures of potential debris flow in Diaolou Gully, Leibo county, Sichuan province[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2017, 28(1):1~6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Google Scholar
|
|
陈炳蔚, 李永森, 符振康.金沙江构造带及邻区的构造变形特征[J].青藏高原地质文集, 1991, 21:222~234.
Google Scholar
CHEN Bingwei, LI Yongsen, FU Zhenkang. Deformations of Jinshajiang tectonic belt and its adjacent areas[J]. Contribution to the Geology of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Platean, 1991, 21:222~234. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Google Scholar
|
|
姚鑫, 许冲, 戴福初, 等.四川汶川Ms8级地震引发的滑坡与地层岩性、坡度的相关性[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(8):1156~1162.
Google Scholar
YAO Xin, XU Chong, DAI Fuchu, et al. Contribution of strata lithology and slope gradient to landslides triggered by Wenchuan Ms 8 earthquake, Sichuan, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(8):1156~1162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Google Scholar
|
|
Colesanti C, Wasowski J. Investigating landslides with space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry[J]. Engineering Geology, 2006, 88(3/4):173~199.
Google Scholar
|
|
Waltham T. Foundations of engineering geology[M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton:CRC Press, 2002.
Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: